Zinc Alloy in Precision Casting Manufacturing
Zinc alloy is a low melting point metal with low melting costs and is easy to shape in the foundry industry. It is commonly used in precision castings such as die casting and gravity casting.

What Is Casting Zinc Alloys?
Zinc alloy is pivotal in precision casting, especially in Consumer Electronics and Telecommunication industries. Its popularity stems from its exceptional properties, notably its corrosion resistance, high thermal conductivity, and precise casting capabilities. In precision casting, where tolerances can be as tight as ±0.01 mm, zinc alloys shine with their ability to maintain such high precision, ensuring intricate components meet exacting standards.
One noteworthy example of zinc alloy's excellence lies in smartphone manufacturing. The precise dimensions of a phone's housing are crucial in the telecommunication sector. Zinc casting allows for intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity. It contributes to the sleek appearance of the device and enhances its durability, showcasing the remarkable applications of zinc alloy in the world of precision casting. Neway's expertise in utilizing zinc alloy for such applications exemplifies their commitment to delivering high-quality solutions.
Properties of Cast Zinc Alloys
Zinc Alloys Chemical Comparison
Zinc alloy is the best metal for die casting and gravity casting because it has a low melting point, good fluidity, and is easy to shape. Zinc alloy die and gravity castings generally have better tolerances and thin-wall properties. Commonly used zinc alloys in Neway include Zamak 2, Zamak 3, Zamak 5, Zamak 7, ZA 8, ZA-12, ZA-35, ACuZinc5, EZAC, ZA 27 - Zinc Aluminum.
Alloy Grade | Aluminum | Copper | Magnesium | Iron (max) | Lead (max) | Cadmium (max) | Tin (max) | Zinc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Zamak 3 | 3.9 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 95.9 |
Zamak 5 | 3.5 | 0.25 | 0.035 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 95.7 |
Zamak 2 | 3.5 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 95.7 |
Zamak 7 | 3.9 | 0.25 | 0.035 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 95.7 |
ZA-8 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 0.02 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 88.0 |
ZA-12 | 11.0 | 1.0 | 0.02 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 86.0 |
ZA-35 | 35.0 | 1.5 | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 58.5 |
ACuZinc5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 91.0 |
EZAC | 4.0 | 1.0 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 92.0 |
ZA 27 | 26.0 | 2.2 | 0.02 | 0.075 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 68.8 |
Function of Chemical Components
Aluminum (Al):
Aluminum is a versatile element in zinc alloys. It primarily serves to enhance the alloy's strength. By forming a solid solution with zinc, aluminum increases the hardness and tensile strength of the alloy. It also plays a pivotal role in promoting the solidification of the alloy. Additionally, in combination with other elements, such as copper, aluminum helps control the grain structure of the alloy, which can be crucial for achieving specific mechanical properties.
Copper (Cu):
Copper is known for boosting tensile strength and hardness in zinc alloys. It enhances the alloy's resistance to wear and corrosion. However, it's essential to manage the copper content carefully. Excessive copper can reduce the fluidity of the molten alloy during casting, potentially leading to casting defects. Thus, maintaining the right balance is crucial to optimize the alloy's properties.
Magnesium (Mg):
Magnesium primarily contributes to the fluidity of the molten zinc alloy. This enhanced fluidity ensures the alloy flows smoothly during casting, filling intricate mold cavities with precision—furthermore, magnesium aids in refining the grain structure of the alloy, leading to improved mechanical properties. Smaller grains generally result in enhanced strength and hardness.
Iron (Fe, max):
While a minimal amount of iron may naturally be present as an impurity, its content is typically controlled to ensure it doesn't exceed specified limits. Excessive iron can detrimentally impact the alloy's corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Keeping iron within acceptable limits is essential for achieving the desired performance characteristics.
Lead (Pb, max):
Lead is typically kept at deficient levels or eliminated in modern zinc alloys, especially those intended for casting. Because lead can lead to brittleness and negatively affect the mechanical properties of the alloy, excess lead is undesirable for achieving the desired casting quality.
Cadmium (Cd, max):
Cadmium is another element restricted or absent in contemporary zinc alloys due to its toxicity. Its presence can compromise the alloy's corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. The reduction of cadmium in alloys aligns with environmental and health safety standards.
Tin (Sn, max):
Like lead and cadmium, Tin is typically maintained at low levels or avoided in casting alloys. An excessive tin content can render the alloy brittle and less suitable for casting applications. Tin is commonly found in non-casting zinc alloys, such as those used in soldering, where its lower melting point is advantageous.
Zinc Alloy Physical and Mechanical Properties
Although there are many grades of cast zinc alloys, differences in their chemical compositions also lead to considerable differences in their properties. Almost every zinc alloy has its particular uses. For example, Zamak 2 is the hardest among the Zamak zinc alloy series. Zamak 3 is the most commonly used zinc alloy for die casting and the most commonly used zinc alloy in North America. Zamak 5 is a zinc alloy widely used in Europe.
Zamak 2 offers good strength and hardness. Suitable for parts requiring intricate shapes. Zamak 3 is widely used due to its balance of strength and flexibility. Suitable for a range of applications, including automotive components and consumer electronics. Zamak 5 offers higher strength and hardness compared to Zamak 3. It's commonly used in the automotive industry for parts that need increased strength. Zamak 7 provides excellent castability and minimal dimensional change. They are used in applications requiring high flexibility, such as decorative hardware.
ZA-8 has high strength and excellent bearing properties. It is commonly used in gears, hydraulic parts, and electrical components.ZA-12 offers superior creep resistance and is often used in applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. ZA-35 provides good strength and impact resistance. They are used in applications like automotive and industrial components. ACuZinc5 is notable for its high copper content. It offers good electrical conductivity. They are commonly used in electrical connectors and electronic applications. EZAC is known for its excellent machinability and castability, often used in automotive, electronics, and telecommunications. ZA 27 - Zinc Aluminum offers high strength and excellent bearing properties. They are used in applications like brackets, handles, and hinges.

Property | Elongation (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength (J) | Hardness (Brinell) | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Electrical Conductivity (% IACS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Zamak 2 | 2 | 250 | 180 | 45 | 70 | 6.6 | 380 | 109 | 27-30 |
Zamak 3 | 3 | 260 | 190 | 50 | 80 | 6.6 | 380 | 109 | 27-30 |
Zamak 5 | 7 | 240 | 180 | 40 | 80 | 6.6 | 380 | 109 | 27-30 |
Zamak 7 | 10 | 240 | 170 | 35 | 80 | 6.6 | 380 | 109 | 27-30 |
ZA-8 | 3-5 | 300-320 | 180-200 | 60-80 | 90-100 | 6.8-7.1 | 380-386 | 109 | 27-30 |
ZA-12 | 3-5 | 320-340 | 200-220 | 70-80 | 90-100 | 6.8-7.1 | 380-386 | 109 | 27-30 |
ZA-35 | 1-2 | 320-340 | 180-200 | 70-80 | 90-100 | 6.8-7.1 | 380-386 | 109 | 27-30 |
ACuZinc5 | 0.5-2 | 170-200 | 140-170 | 15-20 | 65-75 | 6.9-7.3 | 380-386 | 121 | 13-16 |
EZAC | 2-3 | 290-310 | 190-210 | 45-55 | 80-90 | 6.6-7.0 | 380-386 | 109 | 27-30 |
ZA 27 - Zinc Aluminum | 2-3 | 310-330 | 200-220 | 50-60 | 90-100 | 6.5-6.8 | 380-386 | 116 | 17-19 |
Zinc Alloys Precision Casting Features and Applications
As a leading casting manufacturer, Neway has excellent production capabilities, strong scientific and technological capabilities, and rich experience in selecting and customizing materials. We provide zinc alloy die-casting and gravity-casting services to many well-known companies worldwide.

Zamak 2:
Zinc Alloy 2, commonly called Zamak 2 or Kirksite, is recognized for its exceptional strength and hardness within the Zamak alloy family. By ASTM standards, it is classified as ASTM AC43A.
Zamak 2 exhibits superior mechanical properties, making it an ideal choice for precision casting applications. It possesses excellent tensile strength and hardness, ensuring durability and longevity. Its low melting point and exceptional fluidity make it suitable for intricate casting of complex, high-precision parts. Moreover, it showcases excellent surface finish, making it well-suited for applications where aesthetics and precision are paramount. In precision casting, Zamak 2 is extensively utilized for producing a wide range of components, including automotive parts, electronic housings, decorative hardware, and various industrial components. Its high strength and precision casting capabilities enable the creation of intricate, high-precision parts in industries such as Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, Lighting Solutions, Power Tools, and Locking Systems, where exacting standards are imperative.
Zamak 3:
Zamak 3, often called Zinc Alloy 3, is recognized as one of North America's most widely used zinc alloys, bearing the ASTM grade AG40A.
This versatile alloy is favored for its excellent balance of mechanical properties, combining moderate strength, good flexibility, and high impact resistance. With a consistent composition and dependable performance, Zamak 3 is known for its low melting point, facilitating efficient and cost-effective casting. Its corrosion resistance is also valued, making it suitable for various environments.
Zamak 3 is employed across a broad spectrum of precision casting applications. It is commonly utilized in industries such as Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, and Automotive for manufacturing components like intricate casings, connectors, and housing for electronic devices. Its exceptional properties, including ease of machining, make it ideal for creating high-precision parts where reliability and quality are paramount. Zamak 3's versatility and dependability continue positioning it as a top choice in precision casting.
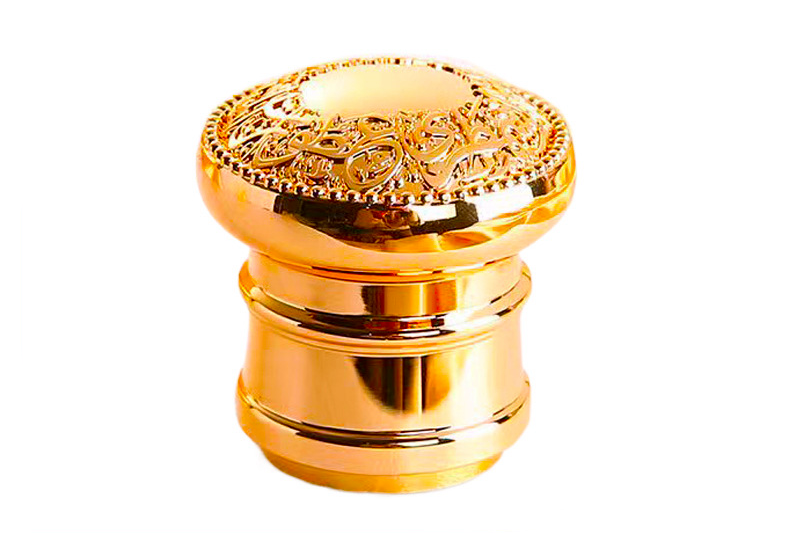


Zamak 5:
Zamak 5(ASTM AC41A), known as Zinc Alloy 5, is recognized as the predominant zinc alloy in Europe, adhering to the ASTM AC41A.
Zamak 5 stands out for its commendable combination of strength and hardness, which makes it a preferred choice for precision casting applications. Its properties make it particularly well-suited for parts requiring higher strength, such as those in the automotive industry. Zamak 5's superior fluidity and low melting point contribute to its precision casting capabilities, allowing for the creation of intricately designed components. Additionally, its corrosion resistance enhances its applicability in diverse environments.
This alloy finds extensive use in precision casting applications, especially in the European market. It is commonly employed in the Automotive industry for producing components that demand enhanced strength and durability. Zamak 5's high-precision capabilities make it suitable for manufacturing parts in sectors like Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, Lighting Solutions, and Power Tools, where exacting standards are crucial. Its widespread acceptance in Europe underscores its reputation as a top-tier alloy for precision casting.
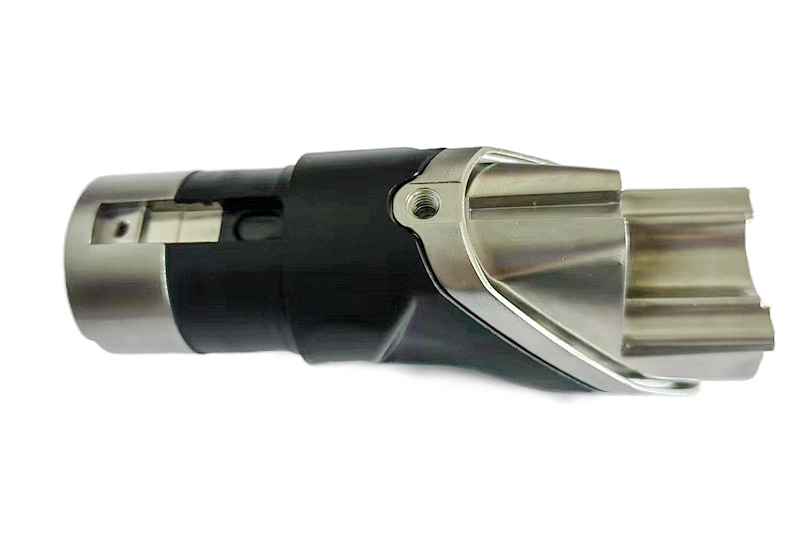
Zamak 7:
Zamak 7, also designated as Zinc Alloy 7 under the ASTM grade AG40B, is a noteworthy modification of Zamak 3. This alloy is recognized for its high purity, ensuring lower magnesium content and stringent impurities specifications.
What sets Zamak 7 apart is its exceptional casting fluidity, improved flexibility, and enhanced surface finish, thanks to its lower magnesium content and rigorous impurities control. This alloy's composition and purity make it an excellent choice for precision casting.
Zamak 7's attributes make it suitable for precision casting in various industries. It finds application in sectors such as Consumer Electronics and Telecommunication, where high-quality casings, connectors, and intricate parts are essential. Additionally, its superior casting fluidity and purity make it valuable in the Power Tools and Locking Systems industries, contributing to producing high-precision components where strength, flexibility, and surface finish are paramount.
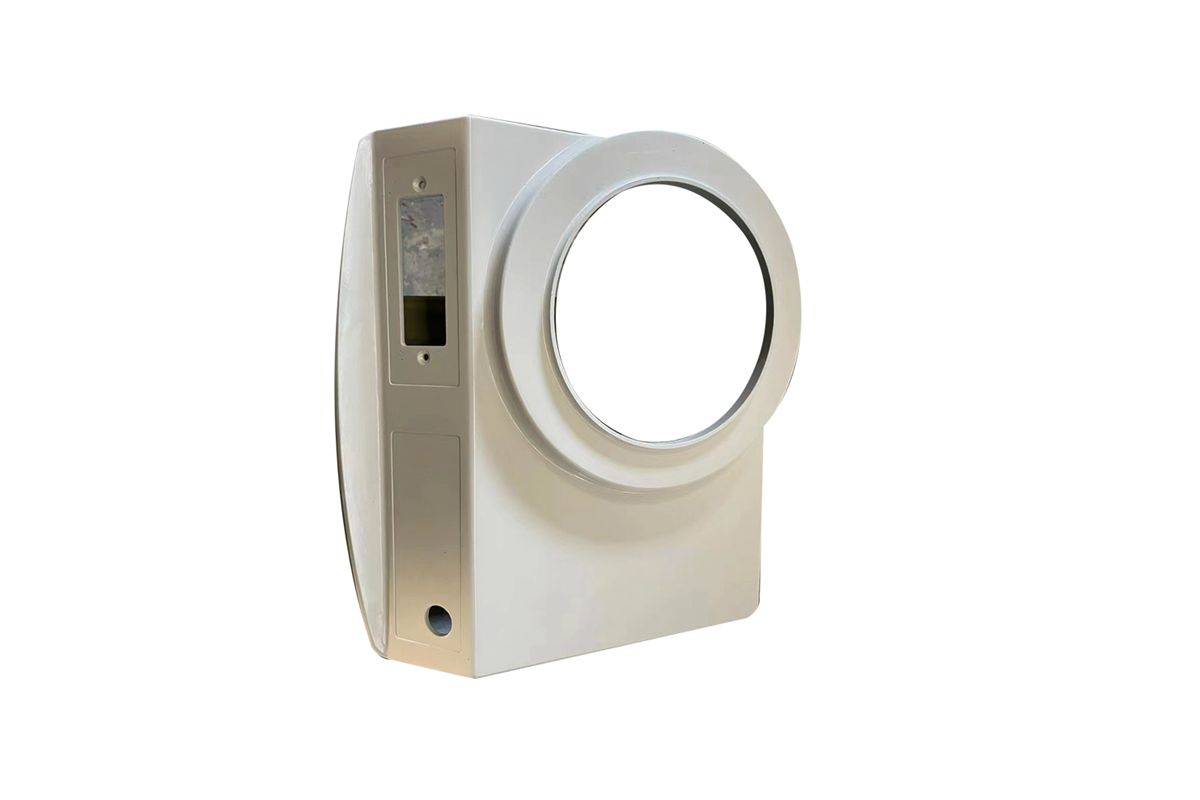


ZA-8:
ZA-8, a zinc-aluminum alloy boasting approximately 8.4% aluminum content, stands out as a unique and essential material in precision casting. One of ZA-8's remarkable features is its higher aluminum content, granting it enhanced strength, durability, and wear resistance. Its exceptional fluidity during casting makes it a prime choice for producing intricately designed components, particularly those that demand precision. Notably, ZA-8 is the sole ZA alloy suitable for hot-chamber die casting. This advantage simplifies the manufacturing process for specific components, eliminating the need for additional steps in production.
In precision casting, ZA-8 plays a pivotal role in various industries. Its high strength and wear resistance make it a favored material for creating durable components in the Automotive sector, such as gearbox parts and brackets. Its precision casting capabilities also find utility in the Consumer Electronics and Telecommunication industries, where intricate and high-precision components like connectors and housing are essential. ZA-8's ability to streamline production, thanks to its compatibility with hot-chamber die casting, positions it as a vital choice for applications where precision, strength, and efficiency are paramount.
ZA-12:
ZA-12, often recognized in the industry as Zinc Aluminum Alloy 12, is prized for its unique attributes and suitability for demanding applications. One of ZA-12's distinguishing features is its superior resistance to creep, making it ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. This alloy's remarkable creep resistance ensures stability and reliability even in demanding thermal conditions. Its composition, balanced zinc, aluminum, and other elements, imparts exceptional casting properties, enabling the production of intricate, high-precision parts. ZA-12's suitability for high-temperature environments, combined with its precise casting capabilities, positions it as an excellent choice for applications where both durability and precision are essential.
ZA-12 is commonly employed in the Automotive sector for manufacturing components exposed to elevated temperatures, like engine parts and exhaust system components. Additionally, its precision casting capabilities serve well in Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, and Power Tools industries, where intricate, high-precision components are essential for product performance and longevity. ZA-12's unique
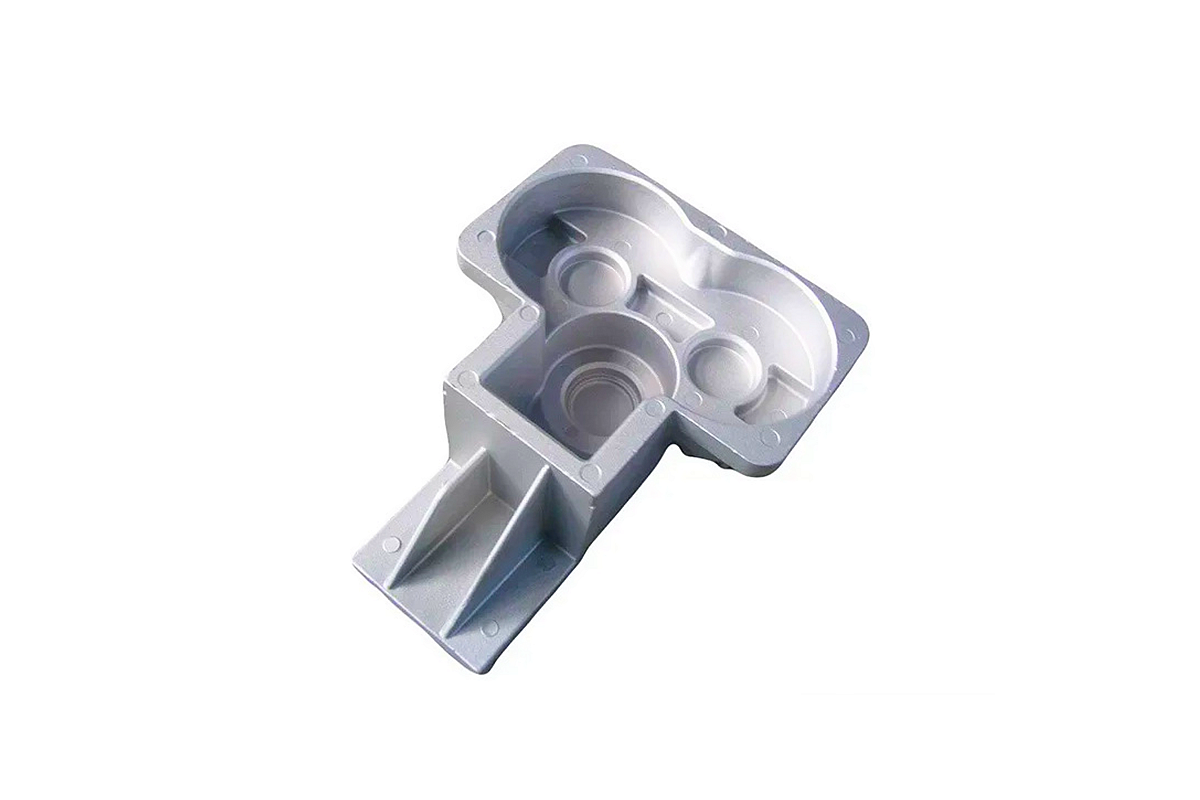

ZA-35:
ZA-35, often called Zinc Aluminum Alloy 35, is a versatile alloy known for its strength and impact resistance, making it an excellent choice for various applications.
One of ZA-35's standout features is its combination of good strength and impact resistance. This alloy offers robust mechanical properties, ensuring the durability of cast components. Its casting properties also make it well-suited for precision casting, facilitating the creation of intricate, high-precision parts. ZA-35's reliability in withstanding impact and consistent composition contribute to its wide range of applications.
ZA-35 is extensively used in precision casting for applications demanding strength and impact resistance. It finds a notable place in the Automotive industry, where it's employed in manufacturing various components, including brackets and structural parts. The industrial sector also benefits from its precision casting capabilities, as ZA-35 produces durable components that can withstand demanding conditions.
ACuZinc5:
ACuZinc5, also known as Zinc-Copper Alloy 5, is an innovative alloy developed by General Motors, celebrated for its unique properties and advantages in die casting and gravity casting applications.
This alloy is renowned for its exceptional creep performance, making it a standout choice in applications requiring long-term stability under elevated temperatures. Additionally, ACuZinc5 exhibits remarkable surface hardness, ensuring durability and wear resistance. Its lubricity, or low friction properties, is a distinctive advantage, reducing friction and wear between moving components. These characteristics collectively make ACuZinc5 an ideal choice for precision die casting and gravity casting, especially for parts that must withstand challenging conditions.
ACuZinc5's remarkable features find applications in diverse industries. In die casting, it is commonly used in manufacturing parts for automotive and industrial sectors, where high-temperature stability, surface hardness, and lubricity are crucial. Its excellence in gravity casting makes it a preferred choice for producing components for power tools and locking systems, ensuring their long-lasting performance.
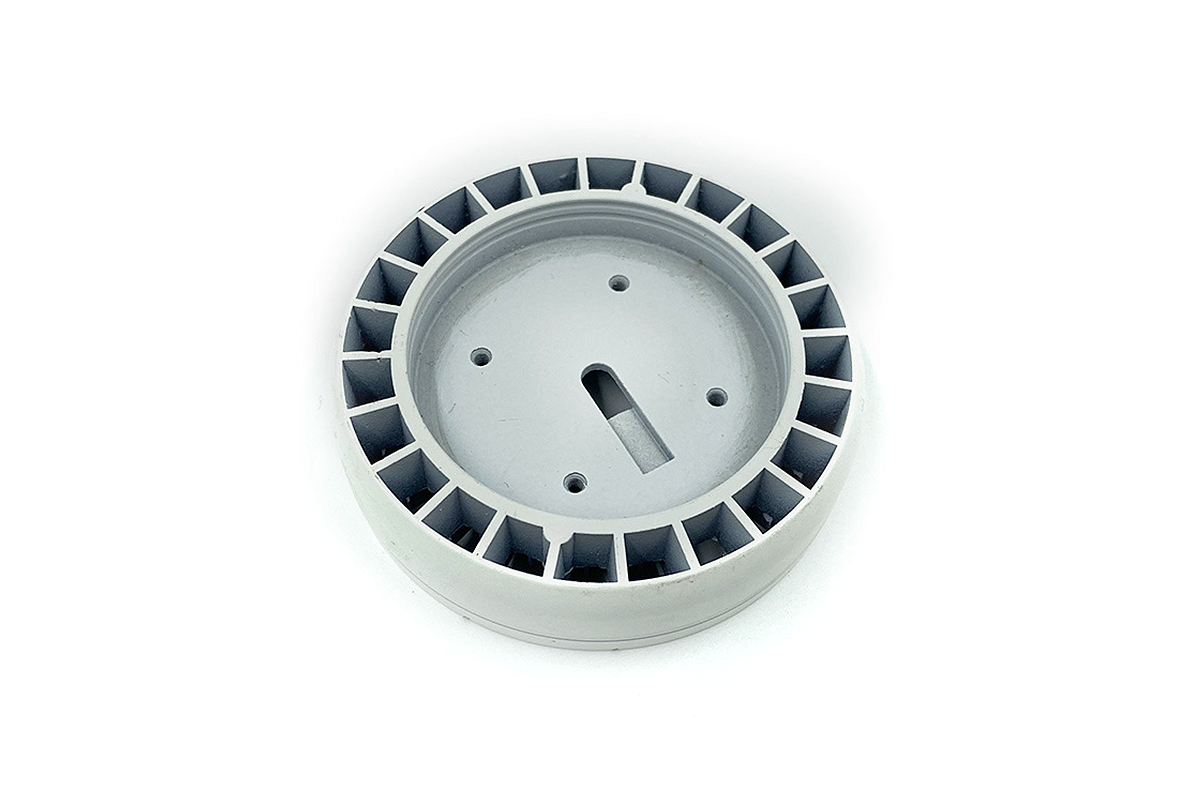
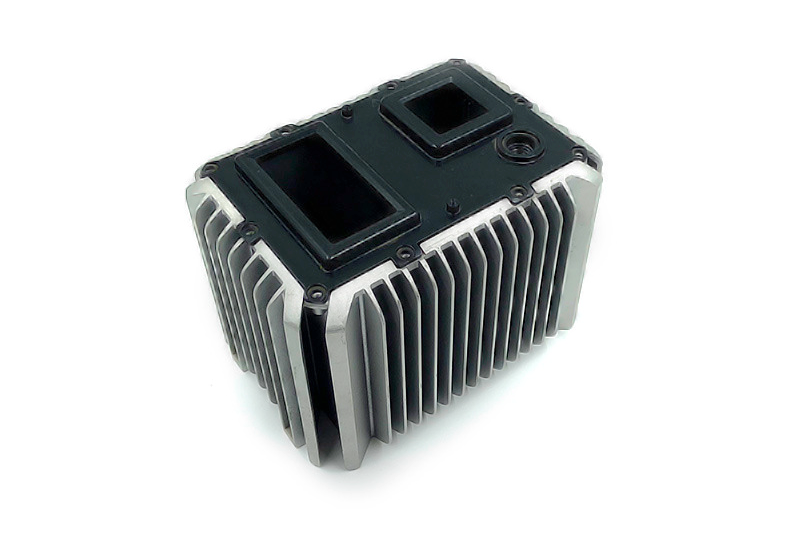


EZAC:
EZAC, often known as Zinc Alloy EZAC, stands out as a high-quality hot-chamber zinc die-casting alloy, prized for its exceptional properties and diverse applications in die casting and gravity casting.
EZAC is distinguished by its superior creep resistance, making it an excellent choice for applications exposed to high temperatures and prolonged stress. This alloy also boasts high yield strength and hardness, ensuring exceptional durability and wear resistance.
EZAC's remarkable features find utility in a range of industries. Die casting is commonly employed in the automotive sector to produce robust engine components and other parts requiring high temperatures and mechanical stress resistance. Furthermore, its excellence in gravity casting is valuable in the aerospace and power tool industries, where precise, high-strength components are crucial for reliable performance.
ZA 27 - Zinc Aluminum:
ZA 27, commonly called Zinc Aluminum Alloy 27, is a distinctive alloy distinguished by its substantial aluminum content, represented by the number 27.
ZA 27 stands out for its remarkable aluminum content, offering exceptional strength and toughness. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it a preferred choice for applications with paramount structural integrity and durability. ZA 27's resistance to corrosion, even in demanding environments, enhances its suitability for die casting and gravity casting.
In die casting, ZA 27 is frequently utilized in producing components for the automotive and aerospace industries, where the combination of high strength, lightweight properties, and precision casting is essential. Its adaptability to gravity casting makes it valuable in producing locking systems, power tools, and lighting solutions, where durability and intricate part design are imperative. ZA 27's exceptional aluminum content and precise casting capabilities make it a reliable choice for applications where strength and precision are pivotal.
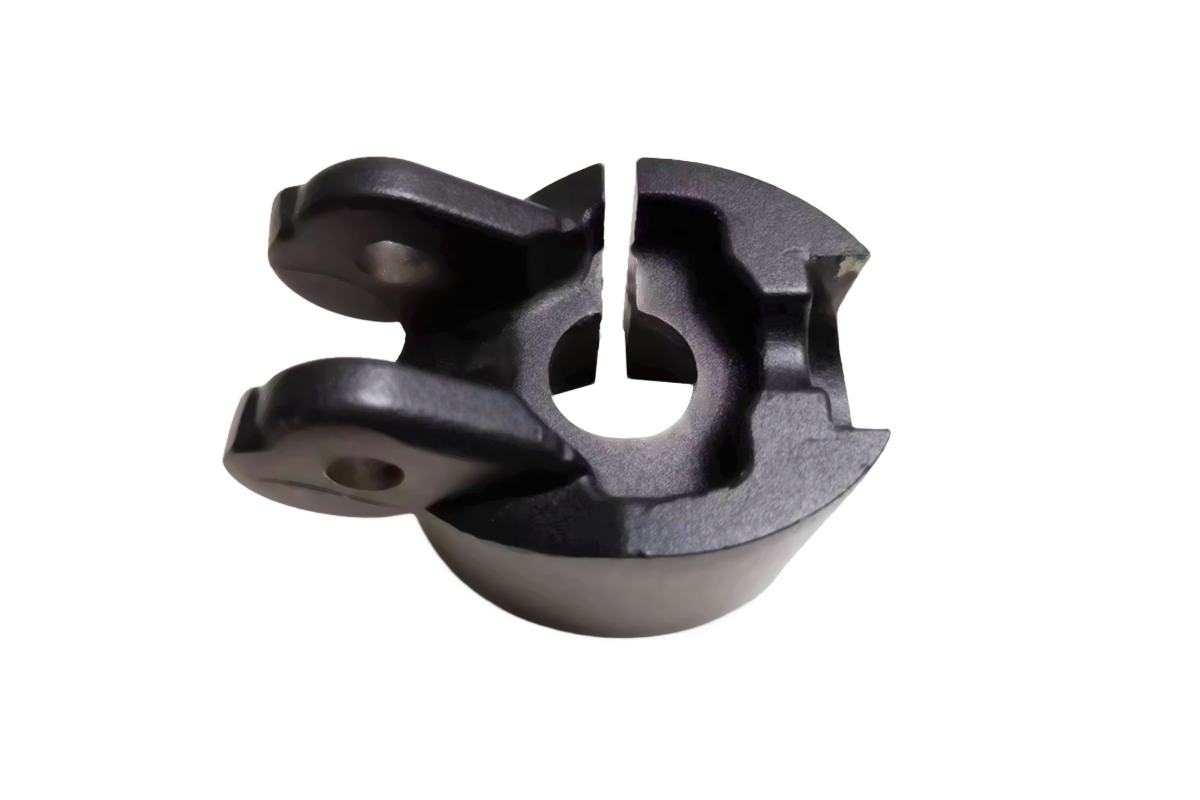

Brand Case Study
Neway has served many world-renowned companies, using its strong manufacturing capabilities and complete quality control system to provide further market competitiveness and quality assurance for major brands.
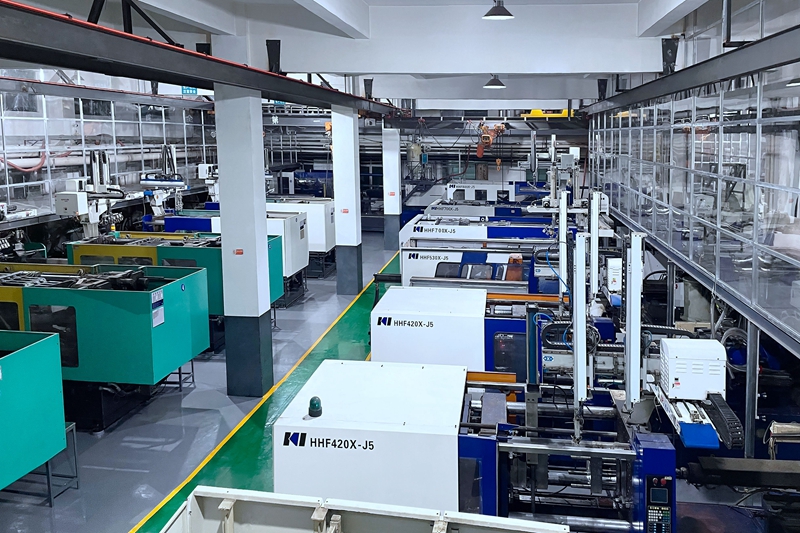
Neway Custom Manufacturing Capability
Neway has gradually improved the production system of basic hardware, plastic, and ceramic non-standard parts after 30 years of growth from the original CNC workshop. As well as polishing, PVD, and simple assembly lines. Provide one-stop, non-standard manufacturing services to our customers.

评论
发表评论