Casting Properties And Applications of A356
A356 is an aluminum alloy primarily used in casting processes and is known for its exceptional properties and versatile applications. As a casting material, A356 offers a remarkable combination of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, making it highly sought after in various industries.
Precision casting, particularly aluminum die casting, finds A356 a preferred material due to its excellent castability. Its properties allow for intricate designs, precise detailing, and fine surface finishes in the manufactured parts. Die casting, utilizing A356, is ideal for creating complex shapes, thin walls, and intricate components, making it a top choice in the automotive, lighting, and consumer electronics industries.
Sand casting with A356 is also prevalent, especially in applications requiring cost-effective production of more significant parts or components. Its fluidity and low shrinkage characteristics make it suitable for creating larger castings with intricate details, making it popular in producing engine components, automotive parts, and structural components.
Gravity casting, another method using A356, is favored for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness in producing high-quality parts. This method suits larger production runs where precision and fine details might be less critical. It finds applications in marine, sporting goods, and general machinery industries.

In summary, A356’s exceptional casting properties make it a versatile choice across various casting methods, offering durability, precision, and cost-efficiency in industries demanding high-quality parts and components. Its applications range from intricate automotive parts to more significant structural components, showcasing its adaptability and reliability in manufacturing processes.
Properties of Cast Aluminum A356
Download PDF: Cast Aluminum A356 Datasheet |
|---|
Chemical Composition of A356
Element | Aluminum (Al) | Silicon (Si) | Magnesium (Mg) | Copper (Cu) | Iron (Fe) | Manganese (Mn) | Zinc (Zn) | Titanium (Ti) | Other Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Composition (%) | 91.0 - 92.6 | 6.5 - 7.5 | 0.20 - 0.35 | 0.20 - 0.35 | 0.10 - 0.35 | 0.05 - 0.20 | 0.05 - 0.20 | 0.05 - 0.20 | ≤ 0.15 |
Function of Chemical Components
Each chemical component in Aluminum A356 plays a crucial role in determining the alloy's properties, casting characteristics, and overall performance.
Aluminum (Al):
Function: As the primary component, aluminum provides the base structure and contributes to the alloy's overall strength and durability.
Silicon (Si):
Function: Silicon enhances fluidity during casting, promoting better fillability of molds. It also improves wear resistance and aids in forming a refined microstructure.
Magnesium (Mg):
Function: Magnesium contributes to the alloy's strength and hardness. It also enhances corrosion resistance and promotes heat treatability, improving mechanical properties.
Copper (Cu):
Function: Copper improves both strength and corrosion resistance. It also enhances the alloy's ability to withstand elevated temperatures, making it suitable for applications in high-temperature environments.
Iron (Fe):
Function: Iron is a common impurity, but it can enhance the alloy's strength in controlled amounts. However, excessive iron content can adversely affect corrosion resistance.
Manganese (Mn):
Function: Manganese is a grain refiner, contributing to the alloy's strength and toughness. It also aids in reducing hot cracking during casting.
Zinc (Zn):
Function: Zinc enhances the alloy's castability and helps control the grain structure. It also contributes to the alloy's response to heat treatment.
Titanium (Ti):
Function: Titanium refines the grain structure and assists in controlling intermetallic phases. It improves mechanical properties and aids in preventing porosity during casting.
Other Elements:
Function: Trace elements, collectively referred to as "Other Elements," are kept to a minimum to prevent impurities. Their presence is carefully controlled to maintain the desired properties of the alloy.
In summary, the chemical components in Aluminum A356 work in synergy to balance strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and castability. Precisely controlling these elements allows manufacturers to tailor the alloy to meet specific application requirements, making A356 a versatile choice in various industries.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Property | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength | Hardness (Brinell) | Shear Strength | Impact Strength | Fatigue Strength | Thermal Conductivity | Density | Melting Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Value (Typical) | 280 MPa | 240 MPa | 75 HB | 170 MPa | 55 J | 130 MPa | 159 W/m·K | 2.68 g/cm³ | 570-640°C |
Typical Applications of Aluminum A356 Castings
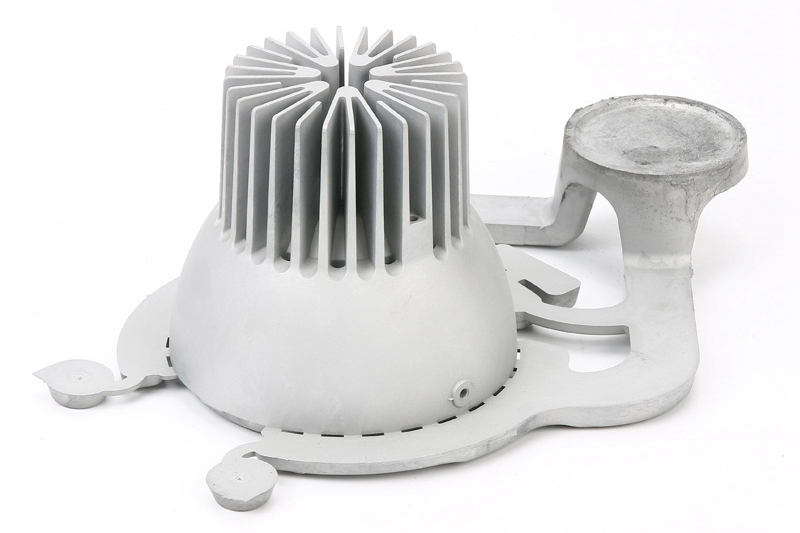
Aluminum A356 Die Casting LED Lighting Heat Sinks
Aluminum A356 die castings are preferred for LED lighting heat sinks primarily due to their exceptional thermal conductivity. The alloy efficiently conducts heat away from the LED components, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. It is crucial in LED applications where heat dissipation is vital for maintaining the longevity and efficiency of the lighting system.
Furthermore, the lightweight and formable nature of the A356 makes it ideal for intricate heat sink designs. The die-casting process allows for the creating of complex geometries that enhance the surface area and promote efficient heat dissipation. This lightweight characteristic is advantageous for LED fixtures, as it contributes to the overall weight reduction of lighting systems.
In addition to its thermal properties, the corrosion resistance of A356 ensures the durability of LED heat sinks in diverse environmental conditions. LED lighting fixtures often operate in various settings, and the ability of A356 to withstand corrosion helps maintain the heat sink's functionality and aesthetics over an extended lifespan. The cost-effectiveness of die casting with A356 further reinforces its suitability for high-volume production of LED heat sinks, making it a pragmatic choice for manufacturers seeking efficiency without compromising performance.
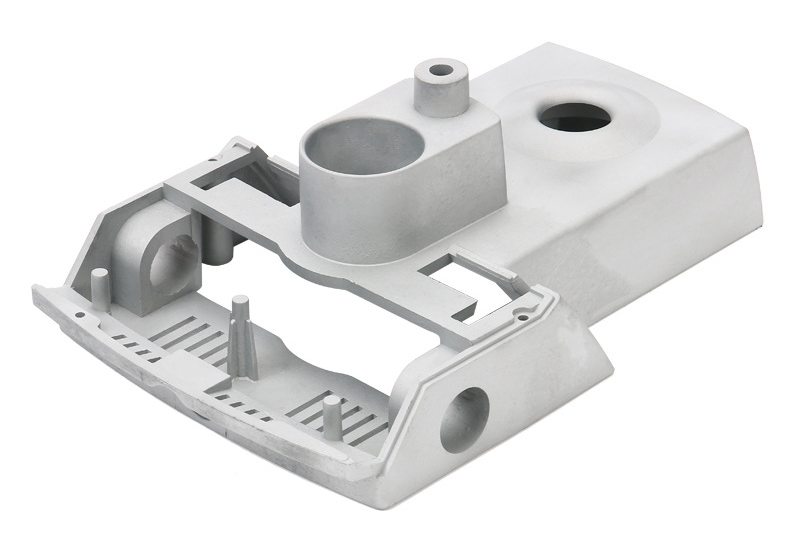


Aluminum A356 Die Casting Electric Device Housings
Aluminum A356 die castings are well-suited for electric device housings owing to a combination of advantageous properties that meet the specific requirements of such applications. Firstly, A356 exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, facilitating the efficient dissipation of heat generated by electronic components within the housing. It is crucial for preventing overheating and maintaining the optimal operating temperature of sensitive electrical devices.
Moreover, the die-casting process allows for creating intricate and precisely detailed housing designs. A356's formability and ability to fill complex molds enable the production of housings with specific features such as heat sinks, ventilation channels, and customized shapes. This versatility in design not only enhances the aesthetics of the electric device but also contributes to effective heat management.
Additionally, A356 die castings offer a lightweight solution without compromising structural integrity. The lightweight nature of the alloy is advantageous for electric devices, contributing to portability and ease of handling. Simultaneously, the robustness of A356 ensures the durability and protection of electronic components, safeguarding them from external environmental factors.
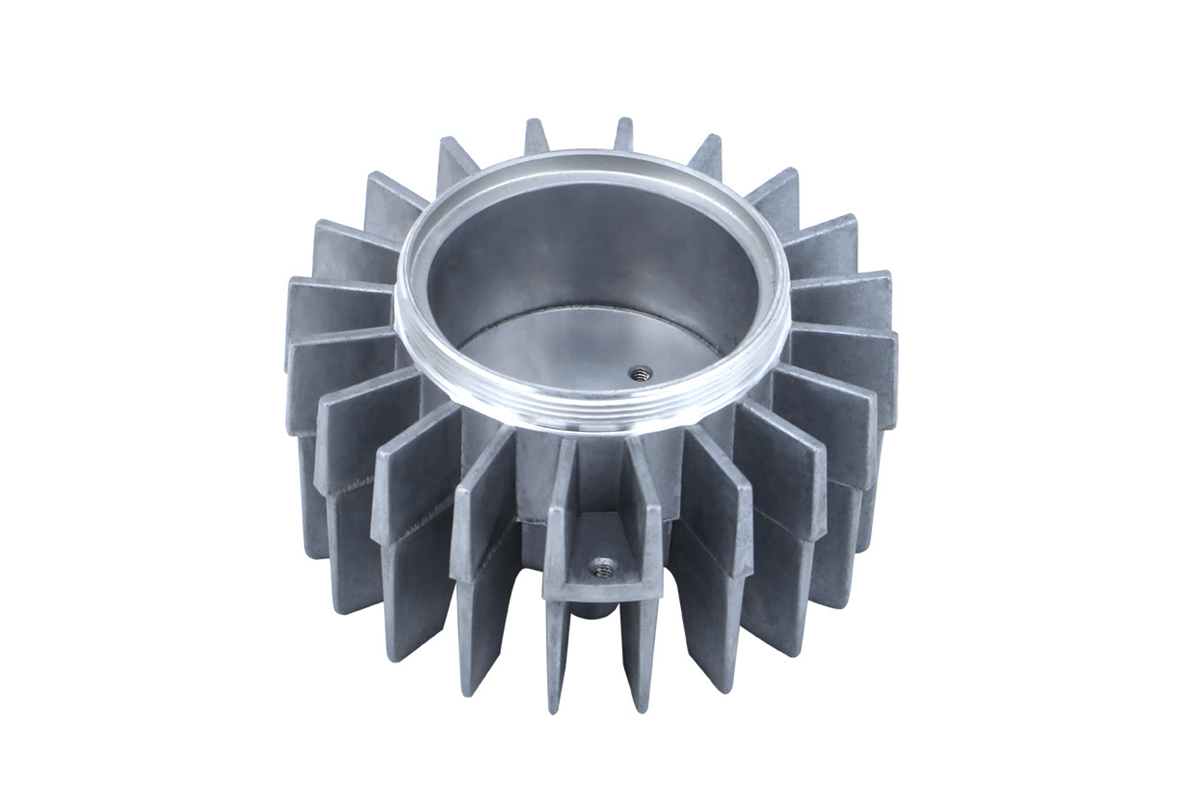
Aluminum A356 Die Casting Automotive Engine Heat Sinks
Aluminum A356 die castings offer optimal solutions for automotive engine heat sinks due to their exceptional properties in precision casting. Precision casting methods, including aluminum die casting, are crucial in manufacturing components like heat sinks, ensuring efficiency and durability.
Precision casting, such as aluminum die casting, provides intricate and complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. It is particularly beneficial for heat sinks in automotive engines, where intricate designs are essential for effective heat dissipation. The A356 aluminum alloy, known for its excellent castability, corrosion resistance, and high strength, further enhances the suitability of die castings for this purpose.
In the context of precision casting, aluminum die castings offer a streamlined production process that facilitates the creation of intricately designed heat sinks with reduced machining needs. It contributes to cost-effectiveness and aligns with Neway's commitment to providing one-stop services for custom parts.
Additionally, using aluminum A356 in die castings ensures efficient heat conductivity, a critical factor in automotive engine applications. The lightweight nature of aluminum aids in optimizing fuel efficiency, addressing a key concern in the automotive industry. Moreover, the ability of A356 to withstand high temperatures makes it an ideal choice for components exposed to the intense heat generated by engines.

Brand Case Study
Neway has served many world-renowned companies, using its strong manufacturing capabilities and complete quality control system to provide further market competitiveness and quality assurance for major brands.
评论
发表评论