Cast Aluminum in Precision Casting Manufacturing
Cast aluminum refers to aluminum alloys that are specifically designed for casting processes such as die casting, investment casting, gravity casting, and sand casting.

What Is Cast Aluminum Alloys?
Cast aluminum refers to aluminum alloys formulated for casting processes like die casting and sand casting. The critical distinction between cast aluminum and standard aluminum lies in their microstructure and properties. Cast aluminum alloys are designed for casting, making them more fluid when molten and enabling the production of intricate shapes and thin-walled structures in cast products. It is achieved by incorporating elements like silicon, which enhances fluidity. In contrast, standard aluminum is typically employed in wrought forms such as sheets and extrusions, known for its excellent strength and corrosion resistance.
Cast aluminum may exhibit slightly lower mechanical properties than wrought aluminum, but it excels in complex casting applications where shape intricacy and design flexibility are paramount. This specialized material ensures that manufacturers can cost-effectively achieve intricate designs, while standard aluminum is favored for its exceptional strength and resistance in more straightforward applications like structural components and industrial sheets.
Properties of Cast Aluminum Alloys
Download PDF: Casting Aluminum Datasheet |
|---|
Chemical Comprison of Cast Aluminum Alloys
There are many die-cast aluminum alloys, and the standards vary from country to country. Most of them are distinguished by the proportion of other elements they contain. For example, the commonly used aluminum-silicon alloy YL113 is code-named LM2 in some countries and is also called 46100, 5076, 384, and 383 or ADC12. Although the names differ, the types of metals they contain are the same. The subtle difference lies in the chemical content.
Alloy | Si (%) | Cu (%) | Mg (%) | Fe (%) | Zn (%) | Mn (%) | Cr (%) | Other Elements (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
6061 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.04 | <0.15 |
6063 | 0.2-0.6 | 0.1 | 0.45-0.9 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | <0.10 |
7075 | 0.4 | 1.2-2.0 | 2.1-2.9 | 0.50 | 5.1-6.1 | 0.30 | 0.18-0.28 | <0.20 |
A356 | 6.5-7.5 | 0.20-0.40 | 0.20-0.45 | 0.20-0.45 | 0.05 | 0.05 | - | <0.10 |
360 | 9.0-10.5 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.35 | 1.0 | 0.10 | - | <0.10 |
A360 | 9.0-10.5 | 0.6 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.60 | 0.20 | - | <0.15 |
380 | 7.5-9.5 | 2.5-3.5 | 0.3 | 1.3 | - | 0.50 | - | <0.10 |
A380 | 7.5-9.5 | 2.6-3.6 | 0.4 | 1.0 | - | 0.50 | - | <0.10 |
383 (ADC12) | 9.0-10.5 | 1.5-3.5 | 0.3 | 1.0 | - | 0.50 | - | <0.10 |
B390* | 9.0-10.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.35 | 1.0 | 0.10 | - | <0.10 |
413 | 11.0-13.0 | 1.0-1.5 | 0.5 | 1.3 | - | 0.50 | - | <0.10 |
A413 | 10.0-12.0 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 1.0 | - | 0.50 | - | <0.15 |
Function of Chemical Components
Silicon (Si):
Silicon promotes castability by reducing the alloy's melting temperature and improving fluidity during casting. It plays a critical role in allowing intricate molds to be filled accurately. Additionally, silicon contributes to the alloy's strength and wear resistance, making it valuable in applications where durability is crucial, such as automotive parts and engine components.
Iron (Fe):
Iron is a stabilizing element that helps control the grain structure in aluminum alloys. It also enhances the machinability of the alloy, making it easier to process into finished products. In this way, iron contributes to the overall workability of aluminum alloys.
Copper (Cu):
Copper increases electrical conductivity, making it advantageous in electrical applications. It also enhances corrosion resistance and adds to the alloy's overall strength. This combination of properties makes copper-containing alloys desirable for electrical connectors, heat exchangers, and other applications where conductivity and durability are essential.
Manganese (Mn):
Manganese contributes to the strength of aluminum alloys and improves workability. It is commonly used in wrought aluminum products like sheets, extrusions, and profiles. The presence of manganese aids in the alloy's formability and resistance to cracking during fabrication processes.
Magnesium (Mg):
Magnesium is a lightweight element that provides strength and impact resistance to aluminum alloys. Its inclusion is particularly valuable in aerospace and automotive applications where weight reduction without sacrificing structural integrity is crucial. It allows the production of lightweight components with excellent mechanical properties.
Zinc (Zn):
Zinc enhances the castability of aluminum alloys and helps control the solidification process during casting. It improves the alloy's strength and hardness. It is often found in applications where intricate shapes and fine details are necessary, such as decorative castings and certain automotive parts.
Tin (Sn):
Tin contributes to the alloy's strength, especially when combined with other elements. It is used in specialized applications, such as manufacturing high-strength aluminum bronzes, which find utility in marine environments where corrosion resistance and durability are paramount.
Other Elements:
Various trace elements can be added to aluminum alloys to achieve specific properties. For example, chromium and nickel are introduced to enhance corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and chemical environments. Titanium is used to refine grain structure, improving the overall mechanical properties of the alloy.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Because aluminum-silicon alloys have good casting properties, high gas properties, simple processes, and excellent corrosion resistance, aluminum-silicon alloys are most commonly used in the die-casting industry at home and abroad. At the same time, aluminum-silicon alloys are also relatively early and widely recognized alloys developed and used in die-casting. After continuous research and improvement, most of the current international mainstream aluminum-silicon alloys have been finalized and are nothing more than A356, A360, A380, ADC12, B390, and A413. , these alloys have similar densities, the same heat capacity, and similar melting points. The primary thermal conductivity, tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation differ.
Select suitable raw materials according to the performance of the target product produced. Among the above alloys, A356 has the highest thermal conductivity, and A380 and ADC12 have the lowest. The tensile limit is the opposite. A360 has the best yield strength and the highest elongation rate.
Among them, the 6061, 6063, and 7075 series of die-cast aluminum can achieve high-demand casting surfaces, such as anodizing, mirror polishing, Etc.
ADC12 performs well in all aspects, is relatively balanced, and has neither outstanding features nor shortcomings. It is a material commonly used in the aluminum casting industry. 80% of Neway Die Casting's products use ADC12. The bearing capacity of the products produced by this material is Strong, has high mechanical properties, good cutting performance, good demolding performance, high casting pass rate, especially friendly for thin-walled parts, and can meet the requirements of high-performance aluminum alloy die castings.

Grade | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Hardness (Brinell) | Shear Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength (J) | Fatigue Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Range (°C) |
6061 | 276 | 241 | 95 | 207 | 24 | 96 | 167 | 2.7 | 582-652 |
6063 | 185 | 145 | 68 | 115 | 17 | 110 | 201 | 2.7 | 606-652 |
7075 | 572 | 503 | 150 | 331 | 32 | 159 | 130 | 2.8 | 477-635 |
A356 | 270 | 200 | 70 | 170 | 35 | 75 | 167 | 2.68 | 540-650 |
360 | 215 | 150 | 60 | 125 | 15 | 75 | 96 | 2.7 | 540-650 |
A360 | 216 | 150 | 60 | 125 | 15 | 75 | 96 | 2.68 | 557-610 |
380 | 260 | 215 | 75 | 165 | 22 | 85 | 156 | 2.73 | 540-660 |
A380 | 310 | 260 | 80 | 186 | 18 | 100 | 149 | 2.72 | 570-640 |
383 (ADC12) | 295 | 255 | 87 | 190 | 25 | 100 | 96 | 2.7 | 570-640 |
B390* | 240 | 215 | 80 | 190 | 15 | 85 | 116 | 2.68 | 593-620 |
413 | 295 | 255 | 87 | 190 | 25 | 100 | 96 | 2.73 | 540-650 |
A413 | 290 | 241 | 84 | 186 | 30 | 90 | 96 | 2.71 | 570-630 |
Key Features and Applications of Cast Aluminum Alloys

Cast Aluminum 6063
Cast aluminum alloy 6063 offers distinct advantages compared to 6061. The key differentiator lies in its improved formability and extrudability, making it an excellent choice for precision casting applications. Its high elongation (25%) and reduced strength compared to 6061 make it particularly suitable for intricate and complex designs. The alloy's superior corrosion resistance and anodizing properties make it ideal for applications requiring a sleek finish, as is often the case in the Consumer Electronics and Lighting Solutions industries. Moreover, its excellent thermal conductivity, around 200 W/m·K, ensures effective heat dissipation in electronic components and lighting fixtures.
In precision casting, 6063 is well-suited for applications where intricate geometries and high-quality surface finishes are paramount. Examples include telecommunication enclosures, where the alloy's superior formability allows for sleek and aesthetically pleasing designs while maintaining structural integrity. Similarly, in the Lighting Solutions industry, precision-cast 6063 components create elegant and efficient lighting fixtures that require intricate shapes and good thermal performance.
Cast Aluminum 6061
Precision casting using cast aluminum alloy 6061 offers distinct advantages. It boasts superior mechanical properties, with a tensile strength of approximately 310 MPa and a hardness of around 95 Brinell, ensuring robust and reliable performance in critical components. Furthermore, cast aluminum 6061 exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity in harsh environments. Its microstructure allows for intricate and complex shapes, enhancing design flexibility and enabling efficient weight reduction. This alloy is particularly renowned for its fine-grain structure, which ensures impeccable surface finishes, making it suitable for components requiring a polished appearance.
Applications of precision casting, utilizing cast aluminum 6061, span various industries. In Consumer Electronics, it's used for lightweight yet durable smartphone frames, providing structural integrity while maintaining a slim profile. In the Telecommunication sector, it plays a pivotal role in crafting intricate antenna components for optimal signal transmission. Precision cast aluminum 6061 is applied in Lighting Solutions to create aesthetically pleasing, high-efficiency LED heat sinks.


Cast Aluminum 7075
Precision casting, especially in the case of cast aluminum 7075, offers remarkable advantages compared to other aluminum alloys. The key features of cast aluminum 7075 include its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, boasting a tensile strength of 83,000 psi, significantly higher than most other aluminum alloys. Its high-precision attributes are showcased in its ability to maintain precise dimensions down to micrometer levels, making it ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances. Furthermore, the alloy's corrosion resistance is exceptional and retains its mechanical properties even in challenging environments.
In terms of applications, precision casting finds its niche across various industries, particularly in those like Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, and Lighting Solutions. For instance, cast aluminum 7075 can be found in high-end smartphone casings in consumer electronics due to its lightweight yet durable nature, ensuring protection while keeping the device sleek. Precision casting is vital for antenna components in the telecommunication sector, where intricate shapes and high precision are critical for signal performance. Lighting solutions benefit from cast aluminum 7075's precision when creating heat sinks for LED fixtures, enhancing efficiency.
Cast Aluminum A356
Cast aluminum A356 is renowned for its exceptional thermal conductivity, making it stand out among casting aluminum alloys. Its thermal conductivity of approximately 150 W/m·K surpasses many other aluminum alloys, ensuring efficient heat dissipation. This property is particularly advantageous in applications where heat management is critical, such as LED lighting fixtures in the Lighting Solutions industry and electric motor housings in Power Tools. The superior thermal conductivity of A356 contributes to extended product lifespan and enhanced performance.
Precision casting, including die casting, gravity casting, sand casting, and investment casting, finds diverse applications across industries. In Consumer Electronics, it's used for crafting intricate and durable smartphone casings. In Telecommunications, precision-cast components facilitate the seamless operation of data transmission equipment. Within Lighting Solutions, finely detailed aluminum light fixtures are created through precision casting, and Power Tools contributes to sturdy yet lightweight tool components. The Locking System industry benefits from precision-cast lock components, ensuring reliability and security.


Cast Aluminum360
360 aluminum alloy, known for its excellent castability, exhibits desirable characteristics, making it an ideal choice for precision casting applications. Its low melting point at around 635°C enables intricate castings. With a nominal composition of 92.85% aluminum, 7% silicon, and small amounts of iron, copper, and nickel, 360 alloy offers superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various industries.
In precision casting, 360 aluminum alloy excels in producing intricate components like consumer electronics heat sinks, precise telecommunication equipment brackets, and lightweight yet durable parts for lighting solutions. Its precision is exemplified by achieving tight tolerances, often within ±0.005 inches, ensuring high-quality, consistent results. Neway leverages the exceptional properties of 360 aluminum alloy to craft parts that meet the demanding requirements of Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, and Lighting Solutions, showcasing our commitment to excellence in precision casting.
Cast Aluminum A360
Cast aluminum A360, compared to cast aluminum 360, offers enhanced properties for various precision casting applications. A360 has a higher silicon content (9-10%) than Al360, resulting in improved fluidity during casting. It leads to a finer surface finish and better corrosion resistance in A360. Moreover, the A360 exhibits superior elongation, making it ideal for complex and thin-walled components.
In precision casting applications, A360 is well-suited for industries such as Consumer Electronics, Telecommunication, and Power Tools. Its enhanced fluidity allows for intricate, high-precision components like smartphone casings and communication device housings. Additionally, A360's resistance to corrosion makes it a reliable choice for power tool parts, ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Its unique properties make A360 a valuable choice for precision casting in these industries, enhancing product durability and quality.
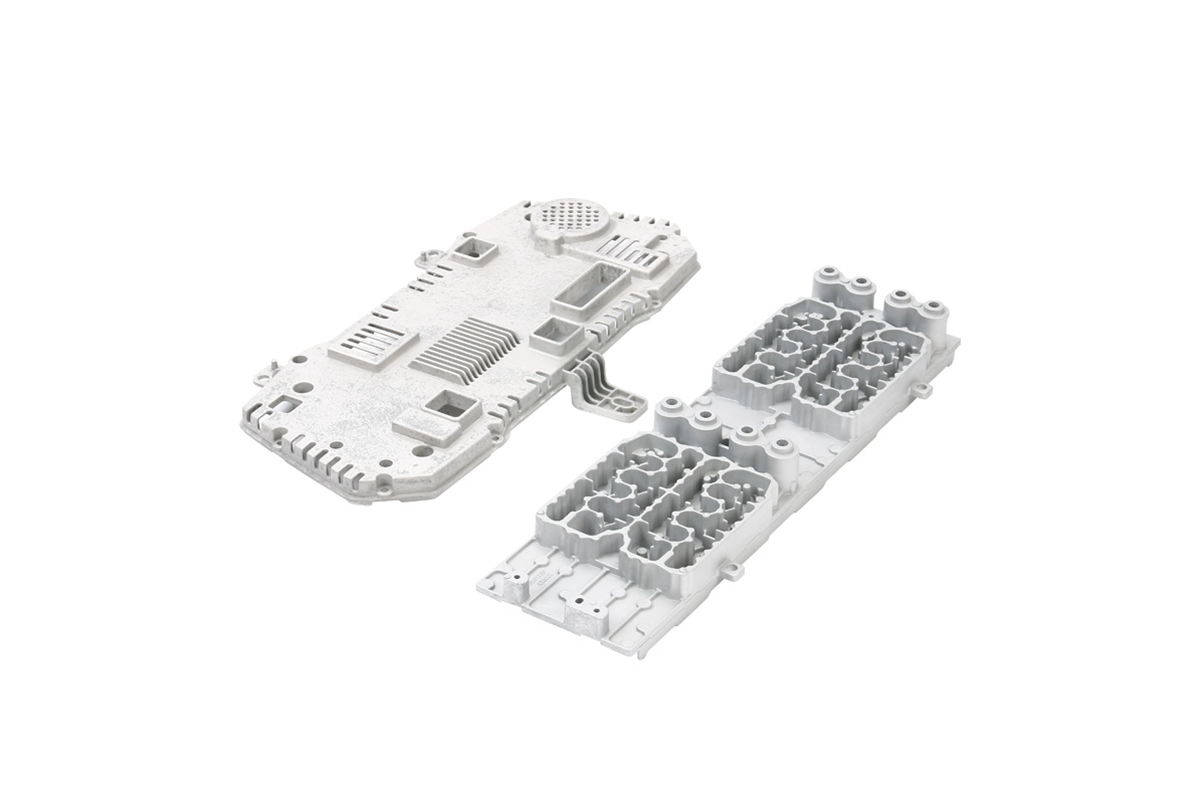

Cast Aluminum 380
Aluminum alloy 380, or A380, is a widely used casting alloy with several distinctive characteristics. It offers excellent castability, making it an ideal choice for precision casting. A380 exhibits good fluidity when molten, ensuring intricate and detailed molds are accurately reproduced. It also features a favorable balance of mechanical properties, with decent strength and ductility. This alloy provides exceptional machining capabilities, enhancing its suitability for precision applications.
A380 is commonly employed in precision casting for a range of applications. Its excellent castability and dimensional stability make it well-suited for producing complex components in automotive, consumer electronics, and lighting solutions. In these applications, A380 can be found in intricate, high-precision parts like housings, brackets, and enclosures, where the alloy's fine detail reproduction and casting quality are highly advantageous.
Cast Aluminum A380
Cast aluminum A380 is a high-performance alloy renowned for its exceptional characteristics compared to standard cast aluminum 380. A380 exhibits superior mechanical properties, including a higher tensile strength of 317 MPa, approximately 25% greater than the 380 alloy, ensuring durability and reliability. Its improved fluidity and lower shrinkage make it ideal for intricate and high-precision components, often achieving a dimensional accuracy of ±0.2 mm.
The A380 is highly favored in precision casting applications, particularly in the consumer electronics and lighting solutions industries. Its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity make it a top choice for heat sinks and LED housings in the lighting sector. Moreover, it's employed for intricate parts like smartphone housings in consumer electronics, thanks to its precise moldability. This superior alloy significantly elevates the quality of precision-cast components, promoting longevity and performance across various industries.
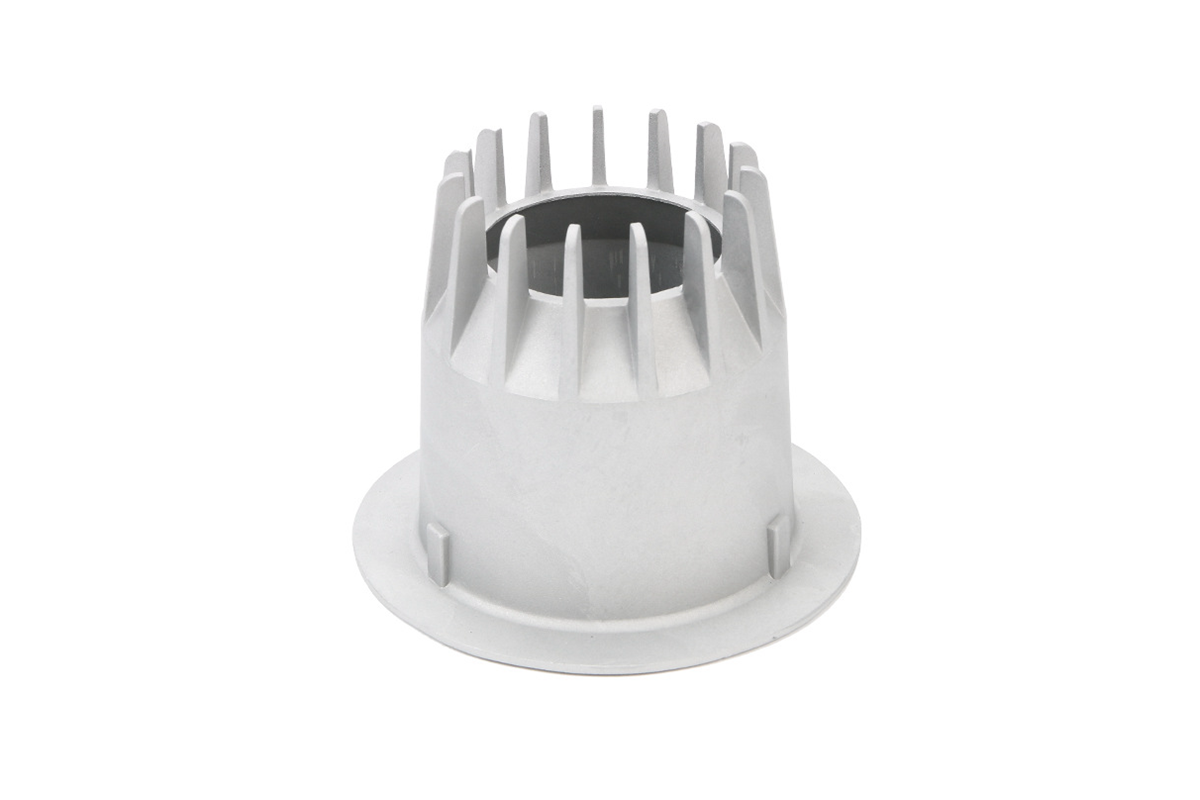
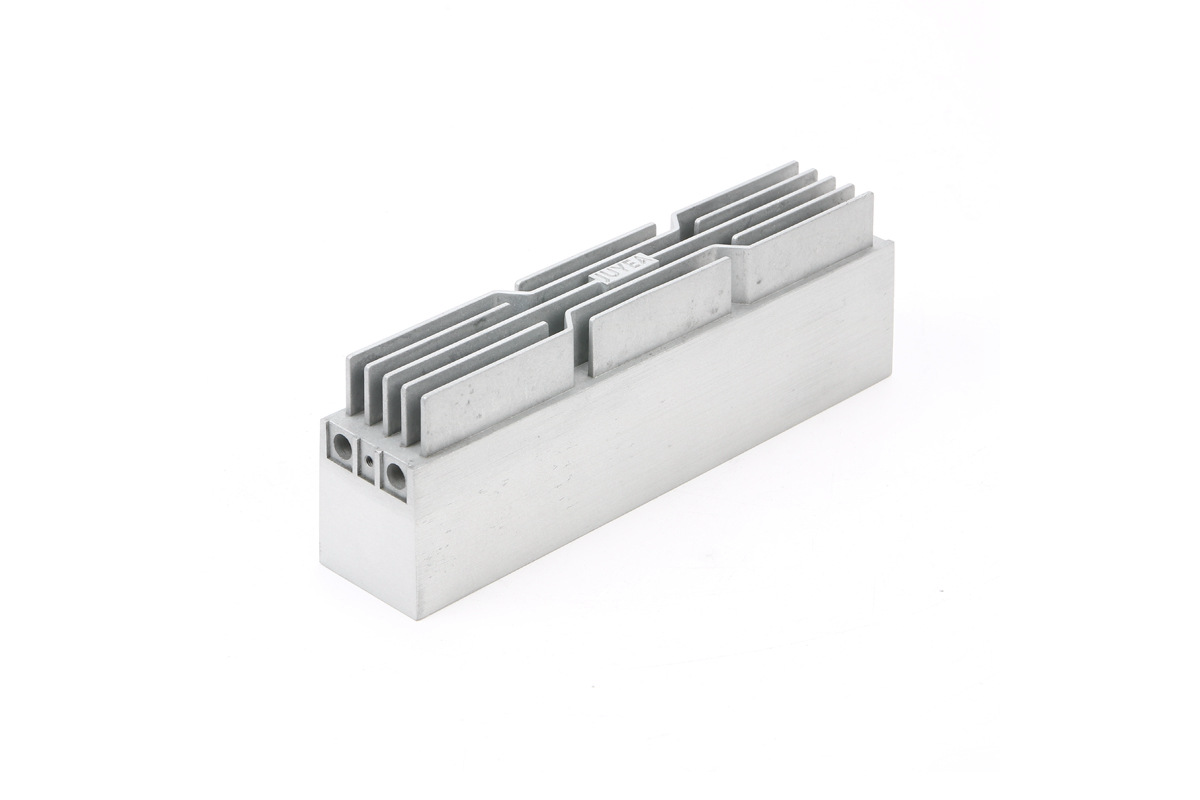


Cast Aluminum 383 (ADC12)
Aluminum alloy 383 is renowned for its excellent casting properties, making it a standout choice in precision casting. Its composition, primarily consisting of aluminum (83%), copper (3.5%), and other elements, offers notable advantages. Its high fluidity allows intricate designs to be faithfully reproduced, even with thin walls and intricate details. Its low melting point, around 635°C, minimizes energy consumption during casting.
This versatile alloy finds its applications in various industries, including Consumer Electronics, where it's employed for precision components in gadgets like smartphones and laptops, ensuring optimal performance. In the Lighting Solutions sector, 383 aluminum alloy is harnessed for producing intricately designed light fixtures. Its high precision, reaching up to ±0.15 mm, is indispensable for crafting secure and reliable lock components in the Locking System industry. Thus, the 383 aluminum alloy is a reliable choice for precision casting across multiple sectors, thanks to its outstanding fluidity, low melting point, and exceptional precision capabilities.
Cast Aluminum B390*
B390* aluminum alloy boasts exceptional characteristics that make it a valuable choice in precision casting. With a precise magnesium and strontium alloying composition, B390* delivers outstanding fluidity and castability, allowing for intricate, high-precision components. This alloy exhibits an excellent combination of mechanical properties, including a tensile strength of up to 390 MPa, making it ideal for applications requiring robust and lightweight components.
In the consumer electronics sector, B390* finds application in crafting finely detailed casings for smartphones, tablets, and laptops, ensuring a sleek appearance and durable build. Telecommunication is crucial in producing intricate signal transmitters and receiver components, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity. Its outstanding precision and mechanical properties make it an indispensable material for crafting compact and high-performance optical and lighting solutions, meeting the demands of modern technology.
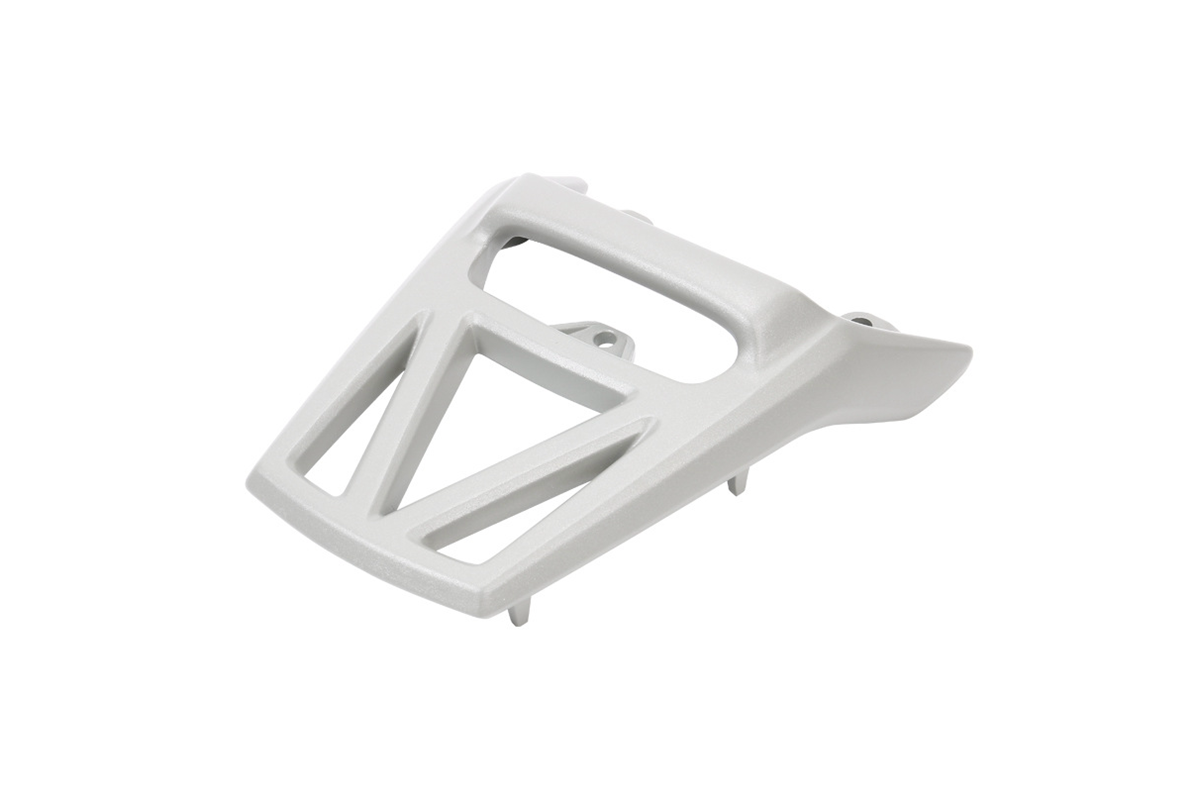


Cast Aluminum 413
Aluminum alloy 413 is renowned for its exceptional properties in precision casting. It boasts excellent fluidity, enabling intricate designs and thin-walled components. With a specific gravity of 2.65 and a melting point of around 587°C, it's ideal for creating lightweight, high-strength parts. Its heat treatability provides versatility, allowing for tailored mechanical properties.
In precision casting, aluminum 413 shines in the Consumer Electronics and Power Tools industries. It's commonly used to craft intricate components like smartphone housings, camera bodies, and power tool casings. Its precision is remarkable, with tight tolerances up to ±0.01 mm, ensuring flawless product assembly. This alloy's superior corrosion resistance makes it an excellent choice for outdoor applications, ensuring long-lasting, durable products in the mentioned industries.
Cast Aluminum A413
Cast aluminum A413, compared to the more common 413 alloys, offers specific advantages in precision casting. A413 is an aluminum-silicon alloy known for its exceptional fluidity during casting, making it ideal for intricate and detailed components. Its silicon content, which ranges from 10.7% to 12.0%, ensures better fluidity and improved casting quality compared to the 413 alloys.
A413 is extensively used in precision casting applications across various industries, including Consumer Electronics and Lighting Solutions. It finds application in crafting complex, lightweight components such as LED light fixtures and mobile device casings in these sectors. The high precision values achieved with A413, typically reaching ±0.5 mm, are crucial in ensuring the tight tolerances and intricate designs required in these industries. Its excellent castability and strength-to-weight ratio make it a top choice for creating intricate, lightweight, and durable components across the Consumer Electronics and Lighting Solutions sectors.

Brand Case Study
Neway has served many world-renowned companies, using its strong manufacturing capabilities and complete quality control system to provide further market competitiveness and quality assurance for major brands.
Neway Custom Manufacturing Capability
Neway has gradually improved the production system of basic hardware, plastic, and ceramic non-standard parts after 30 years of growth from the original CNC workshop. As well as polishing, PVD, and simple assembly lines. Provide one-stop, non-standard manufacturing services to our customers.

#6061,#6063,#7075,#A356,#360,#A360,#380,#A380,#383(ADC12),#B390*,#413,#A413,#PrecisionCasting,#CastAluminumAlloys,#diecasting,#investmentcasting,#sandcasting,#investmentcasting
评论
发表评论