Introduction to Injection Moulding
Plastic Injection molding is widely used for producing large-volume custom plastic parts. It's highly beneficial for mass-production processes where the exact part is being created thousands or even millions of times in succession. The principal advantage of injection molding service is the ability to scale production en masse. Once the initial costs have been paid, the price per unit during injection molded manufacturing is meager. The price also tends to drop drastically as more parts are produced.
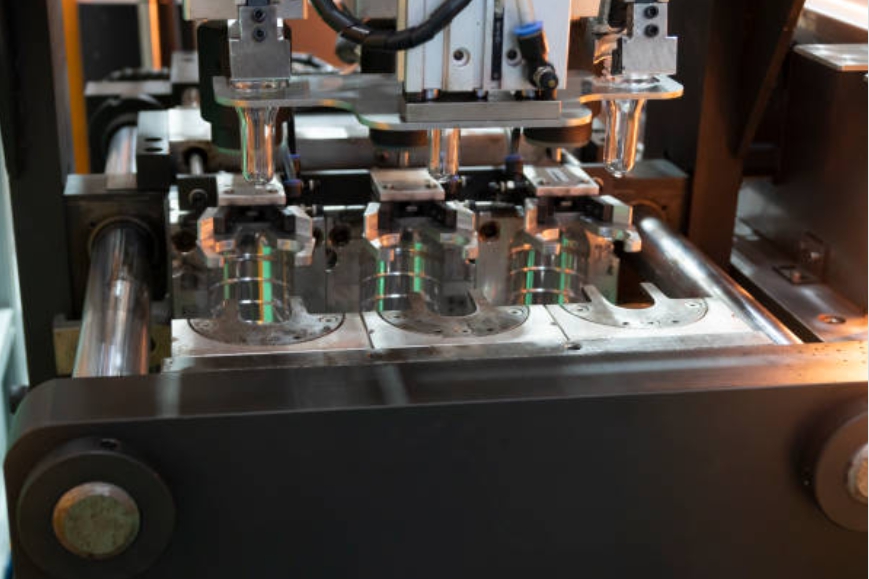
Steps of Plastic Injection Molding
The injection molding process involves six significant steps:
Clamping: The first step in the injection molding process is clamping the mold. It is done to secure and prepare the mold for the material injection.
Injection: The next step is injecting the molten plastic into the mold. The plastic is first melted in the injection molding machine and then injected into the mold, which cools and solidifies into the final part.
Dwelling: After the injection, the molten plastic can dwell inside the cavities. The injection pressure is replaced by the holding pressure in this step to compact the plastic and ensure it fills every mold corner.
Cooling: The cooling process begins once the plastic has been injected and dwelled in the mold. The cooling process is crucial as it allows the plastic to solidify and take the shape of the mold.
Mold Opening: Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold is opened to remove the plastic part.
Removal of Products: The final step in the injection molding process is removing the cooled plastic part from the mold. The part is typically ejected from the mold using ejector pins.
Plastic Injection Moulding Types
Several plastic injection molding processes include plastic injection molding, Two-Shot Moulding, Over molding, Insert molding, and other specialized molding techniques. Each type has its unique benefits and is used for producing specific parts. Choosing the right injection molding process for your custom plastic parts will dramatically reduce costs.
The most common method. Thermoplastic resin pellets are fed into the injection moulding machine, melted, injected into a mould, cooled, and ejected as a solid part. Used for high-volume production of parts.
Two-shot molding, 2K shot molding, or dual-shot molding produces complex moldings from two materials during a single cycle. This process is beneficial when different properties are desired in different areas of the part.

A secondary plastic is an injection molded over a primary plastic part already in the mould. Creates a two-material part with an inner core and outer layer. Used for grips, buttons, seals, etc.
Inserts made of metal, ceramics or other non-plastic materials are placed in the mould cavity first before injection of molten plastic. Useful for electrical or mechanical parts.
Pressurized gas (typically nitrogen) is injected into the molten plastic to create hollow channels and cavities in the part, reducing sink marks and warpage. Used for large, hollow parts.
Water Injection Moulding
Water is injected under high pressure into the molten plastic in the mould, which cools the plastic faster and improves finishes. Fast cycle times.
Foam Injection Moulding
A foaming agent is mixed with the plastic resin, which produces lightweight foam parts. Used for furniture, automotive parts, etc.
Used for thermoset plastics like silicone, polyurethane, and epoxy. Different process than thermoplastic injection moulding.
Injection Molding Machine
An injection molding machine is a complex machinery comprising various components that work harmoniously to create plastic parts. The machine primarily consists of two main parts: the clamping unit and the injection unit.
Clamping unit
The clamping unit holds the mold halves tightly together during the injection process. It applies sufficient clamping force to resist the injection force, keeping the mold halves closed during the injection step until the dwelling step. The clamping unit also ejects the molded part after the dwelling step, opening and closing the mold plates between molding cycles. It ensures that the mold plates are held in proper alignment.
The clamping unit consists of the platen, tie bar, clamping system, and ejection system. The platen holds the mold halves when attached to the injection molding equipment. The tie bar supports the movable plate during translation and aligns the mold plates. The clamping system is responsible for translating the movable platen towards the stationary platen, and the ejection system is responsible for ejecting the molded part.
Injection Unit
The injection unit is where the raw plastic pellets are melted and delivered to the mold. It is responsible for supplying molten plastic to fill the mold cavities, applying heat to melt and homogenize the plastic pellets before injecting them into the mold, and applying sufficient injection pressure and speed to push the molten plastic and fill the mold cavities.
The injection unit consists of the hopper, barrel, heaters, reciprocating screw, and nozzle. The hopper is a large container where the raw plastic pellets are fed. The barrel contains the reciprocating screw and has heaters jacketed on its periphery. The heaters provide thermal energy to melt the plastic pellets to their molten, dense state. The reciprocating screw pushes the plastic through the barrel's length by rotating and sliding axially. The nozzle introduces the molten plastic to the mold cavities.
Plastic Injection Molds
Plastic injection molds play a crucial role in the injection molding process. They are the tools that shape the molten plastic into the desired part. The design and construction of these molds directly impact the final product's quality and manufacturing cost.
The Role and Design of the Mold
The mold's primary role is to form the shape of the plastic part. It consists of two halves that come together to enclose a cavity in the shape of the part. When the molten plastic is injected into the mold, it fills this cavity and takes shape.
The plastic mold design is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of the plastic material being used, the desired shape and features of the part, and the specific requirements of the molding process. The mold must be designed to allow for easy ejection of the part after it has cooled and solidified and to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in the process.
The Concept of Molding
The molding process involves the flow of molten plastic into the mold through a network of channels. These channels, known as the sprue, runners, and cavities, guide the plastic to the part cavities, where it solidifies into the final part.
Sprue, Runner, and Cavities
The sprue is the channel through which the molten plastic enters the mold from the injection machine. The runners are the channels that distribute the plastic from the sprue to the cavities. The cavities are the hollow spaces in the mold that form the shape of the part.
Single and Multiple Cavity Moulds
Molds can be designed with a single cavity to produce one part at a time or with multiple cavities to produce several parts in each cycle. Multiple cavity molds are more complex and expensive but can significantly increase production efficiency for high-volume applications.
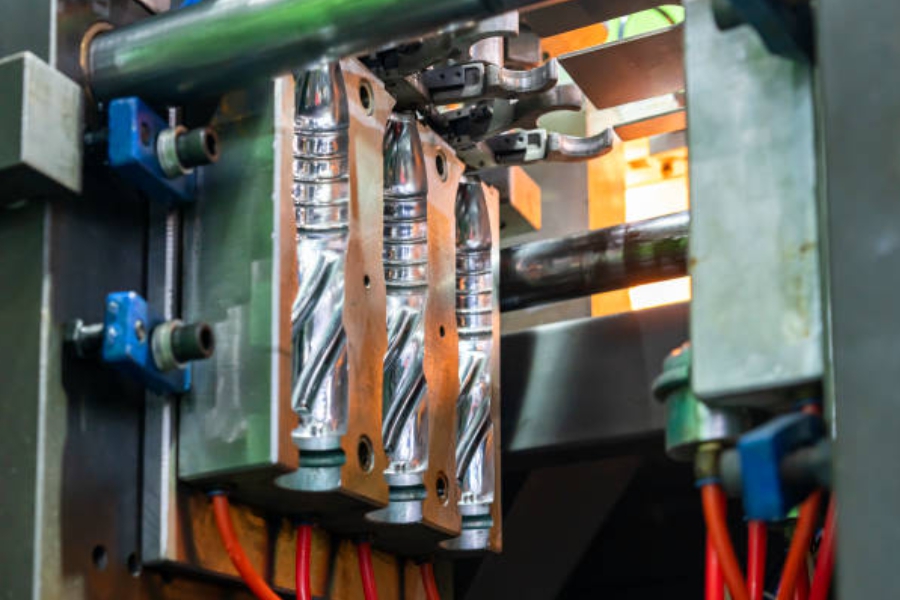

Design Considerations for Multiple Cavities
When designing a multiple-cavity mold, it's essential to ensure that the plastic flows evenly into all cavities. This requires careful design of the runners and gates and may also require using a hot runner injection system to maintain the plastic's temperature.
Molding Conditions on the Final Product
The conditions under which the molding process is carried out can significantly impact the final product's quality. Factors such as the temperature and pressure of the injection, the cooling rate, and the timing of the process steps must be carefully controlled to ensure optimal results.
Mold Construction Requirements
The construction of a mold must be precise and robust to withstand the high pressures and temperatures of the injection molding process. The mold must be made from a material that can resist the corrosive effects of the plastic and the wear and tear of repeated cycles. Common mold materials include hardened steel, pre-hardened steel, aluminum, and beryllium-copper alloy.
The mold must also be designed to allow for efficient cooling. This is typically achieved by incorporating cooling channels into the mold design, through which a cooling fluid can circulate to remove heat from the plastic.
Impact of Mold Design on Its Cost
The cost of a mold is heavily influenced by its design. Complex molds with intricate features or multiple cavities are more expensive than uncomplicated, single-cavity molds. The choice of mold material also affects the cost, with hardened steel molds being more expensive than aluminum ones.
However, while the initial cost of the mold can be high, it can be spread over the large number of parts produced, making the per-part cost relatively low. Furthermore, a well-designed and well-constructed mold can last millions of cycles, making it a worthwhile investment for high-volume production.
The Importance of Mold Materials
The choice of mold material is crucial as it affects the mold's durability, performance, and quality of the parts produced. Hardened steel molds, for example, are highly durable and can produce high-quality parts with excellent surface finish, but they are also expensive and take longer to manufacture. Aluminum molds, on the other hand, are less expensive and quicker to produce, but they may need to be more durable and capable of producing parts with the same level of detail or surface finish.
Neway Mold Assurance
Neway is one of the excellent mold makers. Offers a comprehensive mold assurance program that guarantees the quality and performance of our molds. We use advanced design and manufacturing techniques to produce high-quality molds that meet our customers' specifications. Our experienced engineers work closely with our customers throughout the mold design and production process to ensure their complete satisfaction.
Disposable Mold
In Neway's rapid molding service, rapid molds can be manufactured within 24 hours, and 100% replicas of injection molded parts can be achieved. Although rapid molds are cheap, their life is concise, and usually, only 50 or fewer prototypes can be produced. Rapid tooling technology is suitable for projects that require 100% replicas of the final injection molded product before opening the injection mold.
Low-volume Molds
Neway has the technology to customize mold life according to needs. For example, you only need to inject 500 parts. We can manufacture 500 shot molds to reduce the initial cost. Of course, this is all carried out to ensure the quality of injection molding.
Middle-volume Molds
Neway promises lifetime quality assurance and maintenance on injection molds for medium and high-volume production. No matter how many parts you produce, we provide free mold maintenance service and ensure that the mold is ready for production anytime.
In-House Mold Builds at Neway
At Neway, we specialize in in-house mold builds. Our experienced engineers and technicians work closely with our customers to design and build molds that meet their specific requirements. We use advanced CAD/CAM software and CNC machining equipment to ensure precision and quality in every mold we produce.
Insert Molds
Insert molding service involves injecting plastic around an insert made of a different material. The insert can be a simple object, like a metal rod, or a complex assembly of multiple parts. The resulting product is a single piece with the insert encapsulated by the plastic. This process is often used to create parts that combine metal's strength with plastic's flexibility and versatility.

Free Standing Molds
Free-standing molds are designed to be used without a supporting structure. They are typically made from robust materials like steel or aluminum and are used for producing large parts or parts with complex geometries.
Plastic Injection Molding Cost Composition
The cost of plastic injection molding comprises several factors, including mold cost, materials cost, injection cost, and costs associated with quality control and packing.
Mold Cost
The mold cost is one of the most significant expenses in plastic injection molding. This includes the cost of designing and manufacturing the mold. The mold cost can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the part, the number of cavities in the mold, and the type of mold material used.
Ways to Reduce the Mold Cost
There are several ways to reduce the mold cost. One is to simplify the part design as much as possible, reducing the complexity of the mold. Another is to use a mold material that offers a good balance between cost and performance. Additionally, optimizing the mold design for the manufacturing process can reduce waste and improve efficiency, further reducing costs.
Materials cost
The materials cost includes the cost of the plastic resin used in the molding process. The cost of the resin can vary depending on the type of plastic used, the market price of the plastic, and the quantity required.
Injection Cost
The injection cost includes operating the injection molding machine and the labor cost associated with the injection process. This cost can be influenced by factors such as the cycle time, the complexity of the part, and the machine's efficiency.
QC and Packing
Quality control (QC) and packing are significant cost factors in plastic injection molding. QC involves inspecting the parts to ensure they meet the required specifications, while packing involves preparing the parts for shipment. These processes require time and labor, which add to the overall cost.
Common Plastic Injection Molding Materials
Various materials can be used in plastic injection molding, each with unique properties and applications. Here are some of the most common ones:

Acrylic (PMMA) Injection Molding
Properties: Acrylic, also known as PMMA, is a clear, rigid plastic that resembles glass. It has excellent weather resistance, is stable over various temperatures, and resists UV light and impact.
Applications: Acrylic is often used when a clear, durable plastic is required, such as windows, skylights, and signs.
Grades and Brands:
PMMA Grade | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Plexiglas® (General-Purpose PMMA) | Optical clarity, ease of molding | Transparent displays, signs, automotive lenses |
Altuglas® (High-Impact PMMA) | High impact resistance, clarity | Safety shields, aircraft windows, instrument panels |
Optix® (Optical-Quality PMMA) | Superior optical clarity | Optical lenses, camera lenses, medical devices |
Lucite® (High-Performance PMMA) | Strength, UV resistance | Architectural glazing, lighting fixtures, aircraft windows |
Acrylite® (UV-Resistant PMMA) | UV protection, optical clarity | Outdoor signage, protective barriers, skylights |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Injection Molding
Properties: ABS is a rigid, impact-resistant plastic that is easy to mold and has good dimensional stability.
Applications: ABS is commonly used in various applications, including automotive parts, toys, and consumer electronics.
Grades and Brands:
ABS Grade | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
General-purpose ABS | Versatile, good balance of strength and impact resistance, easy to process. | Consumer products, automotive interior parts, toys. |
High-impact ABS | Enhanced toughness and excellent impact resistance. | Safety equipment, automotive exterior components. |
Flame-retardant ABS | Self-extinguishing meets fire safety requirements. | Electrical enclosures, appliance housings. |
UV-stabilized ABS | Resistant to UV degradation, suitable for outdoor use. | Outdoor signage, automotive exterior parts. |
Nylon Polyamide (PA) Injection Molding
Properties: Nylon, or polyamide (PA), is a robust and flexible plastic with excellent resistance to wear, heat, and chemicals.
Applications: Nylon is often used in applications where durability and flexibility are required, such as gears, bushings, and automotive parts.
Grades and Brands:
Grade | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
PA6 | High toughness, good impact resistance | Automotive parts, gears, bearings |
PA66 | Excellent strength, stiffness, and heat resistance | Structural components, electrical connectors |
PA11 | High flexibility, resistance to chemicals | Fuel lines, hoses, cable insulation |
PA12 | Low water absorption, good chemical resistance | Medical devices, packaging materials |
PA46 | Exceptional heat resistance, mechanical strength | High-performance engineering applications |
Polycarbonate (PC) Injection Molding
Properties: Polycarbonate is a robust and rugged material with high impact resistance. It also has excellent transparency and can be molded into complex shapes.
Applications: Polycarbonate is commonly used in applications that require transparency and high-impact resistance, such as eyewear, medical devices, and automotive components.
Grades and Brands:
Grade | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Polycarbonate (PC) | High impact resistance, optical clarity, and excellent electrical insulation. | Safety helmets, eyeglass lenses, medical devices. |
Lexan PC | Exceptional strength, UV resistance, flame retardant. | Aerospace components, automotive lighting. |
Makrolon PC | High stiffness and excellent dimensional stability. | Electrical connectors, machine guards. |
Calibre PC | Excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption. | Food containers, medical devices. |
LEXAN 9034 PC | High heat resistance, optical clarity. | Signage, machine guards, face shields. |
Polyethylene (PE) Injection Molding
Properties: Polyethylene is a lightweight, durable plastic with excellent chemical resistance. It's available in various densities, with high-density polyethylene (HDPE) being more substantial and more rigid and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) being more flexible.
Applications: Polyethylene is used in various applications, including packaging, containers, pipes, and toys.
Grades and Brands:
Polyoxymethylene (POM) Injection Molding
Properties: Polyoxymethylene, or acetal, is a high-strength, low-friction engineering plastic with excellent wear properties. It's also resistant to water, heat, and chemicals.
Applications: POM is often used in precision parts requiring high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability, such as gears, bearings, and fasteners.
Grades and Brands:
POM Grade | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Delrin® | - Versatility - High stiffness - Excellent dimensional stability | Gears, bushings, fasteners, automotive components |
Delrin® AF | - Low friction - Wear resistance - PTFE-filled | Bearings, bushings, conveyor systems, moving parts |
Delrin® 570 | - FDA-compliant - Good chemical resistance | Food processing equipment, medical devices, conveyor belts |
Hostaform® | - Engineering properties - High strength | Automotive parts, precision gears, electrical components |
Celcon® | - Low friction - High wear resistance | Low-friction bearings, conveyor components, pump parts |
Polypropylene (PP) Injection Molding
Properties: Polypropylene is a lightweight, heat-resistant, and flexible plastic. It has excellent resistance to electricity and is commonly used in products that require heat resistance, electrical insulation, and a low cost.
Applications: Polypropylene is used in various applications, including packaging, textiles, automotive parts, and reusable containers.
Grades and Brands:
PP Grade | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
PP Homopolymer | - Stiffness - High chemical resistance - Cost-effective | Automotive parts, containers, packaging, toys |
PP Copolymer | - Impact resistance - Good flexibility - Versatility | Automotive bumpers, appliance components, sports equipment |
PP Random Copolymer | - Transparency - Good impact resistance - Versatility | Food packaging, clear containers, medical components |
PP Glass-Filled | - Enhanced strength - Stiffness - Dimensional stability | Automotive interiors, industrial parts, structural uses |
PP Homopolymer with UV Stabilization | - UV resistance - Stiffness - Weather resistance | Outdoor furniture, garden equipment, automotive exterior |
Polystyrene (PS) Injection Molding
Properties: Polystyrene is a rigid, brittle plastic often used in disposable products due to its low cost. It is available in both a general-purpose form and a high-impact form that is more durable.
Applications: Polystyrene is commonly used in disposable cutlery, plastic models, CD cases, and other consumer products.
Grades and Brands:
PS Grade | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
General-Purpose PS | - Good clarity - Rigidity - Affordability | Packaging, disposable utensils, consumer goods |
High-impact PS (HIPS) | - Enhanced impact resistance - Good rigidity - Moderate cost | Toys, automotive parts, refrigerator interiors |
Crystal PS (CPS) | - Exceptional clarity - Optical quality - Brittle | Optical lenses, CD jewel cases, clear packaging |
High Heat PS (HHPS) | - Enhanced heat resistance - Retains clarity - Higher cost | Microwave-safe containers, food service trays |
Flame-Retardant PS (FRPS) | - Flame resistance - Low smoke emissions - Electrical insulating properties | Electrical enclosures, automotive interiors, safety equipment |
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Injection Molding
Properties: Thermoplastic elastomers are a type of plastic that combines the properties of elastomers (rubbers) with the processability of thermoplastics. They are flexible, durable, and can be molded into various shapes.
Applications: TPEs are often used in applications that require flexibility and durability, such as seals, gaskets, and soft-touch grips.
Grades and Brands:
TPE-TPV Grade | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
General-Purpose TPE-TPV | - Flexibility - Resilience - Ease of processing | Seals, gaskets, automotive interior components |
High-Elasticity TPE-TPV | - High stretch and rebound properties - Elasticity | Medical tubing, sportswear, shock-absorbing components |
Oil-Resistant TPE-TPV | - Resistance to oils and chemicals - Durability | Automotive hoses, industrial seals, conveyor belts |
UV-Resistant TPE-TPV | - Resistance to UV radiation - Weather resistance | Outdoor equipment, automotive exterior parts |
Soft-Touch TPE-TPV | - Comfortable tactile feel - Softness - Flexibility | Grip handles, consumer electronics, medical devices |
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Injection Molding
Properties: Thermoplastic polyurethane is a versatile plastic that offers high elasticity and transparency, as well as resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion.
Applications: TPU is commonly used in applications that require flexibility, durability, and transparency, such as phone cases, medical devices, and automotive parts.
Grades and Brands:
TPU Grade | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
General-Purpose TPU | - Good balance of flexibility and toughness - Abrasion resistance - Chemical resistance | Seals, gaskets, footwear, automotive components |
High-Elasticity TPU | - Exceptional elasticity and resilience - High tear strength | Shock-absorbing components, medical tubing, sportswear |
Wear-Resistant TPU | - Excellent abrasion resistance - Durability - Low-temperature flexibility | Conveyor belts, industrial wheels, footwear |
UV-Resistant TPU | - Resistance to UV radiation and weathering - Outdoor durability | Outdoor equipment, automotive exterior parts |
Flame-Retardant TPU | - Flame resistance - Low smoke emissions - Electrical insulating properties | Fire safety equipment, electrical enclosures |
Plastic Injection Molding Material Selection
Material selection plays a crucial role in the success of a plastic injection molding project. The chosen material must meet the functional and aesthetic requirements of the part, be compatible with the molding process, and fit within the project's budget. A thorough understanding of the properties and advantages of different materials can help make an informed material selection.
Plastic Parts Surface Treatment
Plastic Injection Molding Pros and Cons
Like any manufacturing process, plastic injection molding has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you determine if it's the proper process for your project.
Advantages of Injection Moulding
1. High Production Speed: Injection molding is a fast process for high production rates. Once the initial setup is complete, the process can produce thousands of parts in a short amount of time.
2. Complex Part Design: Injection molding allows for the production of complex and intricate parts. The process can handle complex geometries and a wide range of sizes.
3. High Efficiency: Injection molding is a highly efficient process with a low scrap rate. The process allows for the use of regrind, further reducing waste.
4. Material and Color Flexibility: Injection molding allows for the use of a wide range of materials and colors. This flexibility makes it possible to produce parts with specific properties and aesthetics.
Disadvantages of Injection Moulding
1. High Initial Costs: The initial cost of an injection molding machine and the creation of molds can be high. However, these costs can be spread over many parts, reducing the cost per part.
2. Part Design Restrictions: While injection molding can handle complex part designs, there are some restrictions. For example, parts with very thin walls or complex undercuts may be difficult or impossible to produce.
3. Limited Material Choices: While many materials can be used in injection molding, not all materials are suitable. Some materials may not have the necessary flow characteristics or may degrade at the temperatures used in the process.
8. Plastic Injection Moulding Consideration.
When planning a plastic injection moulding project, several key considerations must be remembered.
Financial Considerations
The financial aspects of a project are always a significant consideration. This includes the cost of the injection moulding machine, the molds, the materials, and the labor. It's essential to consider the project's total cost, including the initial investment and the ongoing production costs.
Production Quantity
The quantity of parts to be produced is another vital consideration. Injection moulding is most cost-effective for high-volume production runs, where the initial costs can be spread over many parts. For low-volume production, other manufacturing methods may be more cost-effective.
Design Factors
The design of the part is a critical factor in injection moulding. The part must be designed to be easily mouldable, considering factors such as wall thickness, draft angles, and undercuts. The part's design can also affect the choice of material and mold design.
Production Considerations
Production considerations include factors such as the cycle time, the efficiency of the machine, and the quality control processes in place. These factors can affect the cost and quality of the final parts.
Efficiency of Injection Moulding
Despite its challenges, injection moulding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process. It allows for producing various parts in various materials and colors, from simple to complex. With careful planning and consideration, it can be a cost-effective solution for high-volume production.
Applications of Plastic Injection Mouldings
Plastic injection moulding is used in a wide range of industries and applications. Here are a few examples:
Automotive Industry: The automotive industry uses injection moulding to produce various parts, from interior components like dashboard elements and knobs to exterior parts like bumpers and grilles. The process allows for the production of complex parts in various materials, making it ideal for the diverse needs of the automotive industry.

Medical Industry: Injection moulding is used extensively in the medical industry to produce a wide range of products, from surgical instruments to implantable components. The process allows for the production of exact and consistent parts, which is crucial in medical applications.
Consumer Products: Many products are produced using injection moulding, including toys, household appliances, and electronic devices. The process allows for the production of parts in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors, making it ideal for the diverse needs of the consumer product market.
Packaging Industry: Injection moulding is used in the packaging industry to produce containers, lids, and other packaging components. The process allows for the production of parts with high precision and consistency, which is crucial in packaging applications.
In conclusion, plastic injection moulding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process in various industries and applications. With careful planning and consideration, it can be a cost-effective solution for high-volume production.
Plastic Injection Molding Material Optional
Thermoplastics | Thermosets | |||
Medical-Grade silicone rubber | ||||
Optical silicone rubber | ||||
评论
发表评论