The metal bending process is a sheet metal fabrication process. When metal is bending, each material has a minimum angle it can be bent before fracturing. The flexibility and hardness of the metal influence the minimum bend angle. Exceeding the minimum bending capability leads to cracks and breakage. Below are details on approximate minimum inside bend angles for common metals, assuming proper radii:
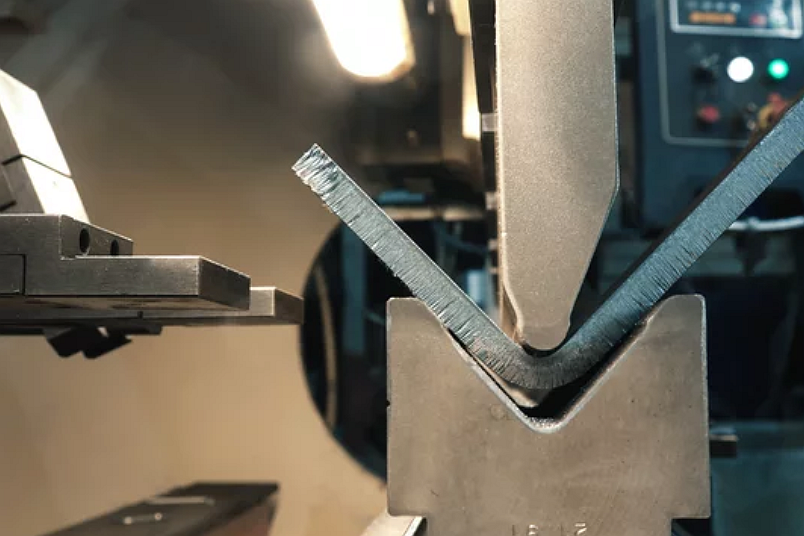
Mild Steel
Mild steel is the most commonly bending metal, valued for its excellent formability and strength. The minimum bend angle for mild steel depends on its thickness and grade:
- 16 gauge (.060"): minimum bend angle around 35 degrees
- 14 gauge (.075"): minimum bend angle around 40 degrees
- 12 gauge (.105"): minimum bend angle around 50 degrees
- 3/16" (0.1875"): minimum bend angle around 60 degrees
- 1/4" (0.25"): minimum bend angle around 70 degrees
The minimum angle increases for thicker mild steel because more elongation and compression are required to deform it without fracturing. Annealed mild steel can bend slightly sharper than higher strength grades. Proper inside radii relative to thickness are essential.
Aluminum
Aside from particular hard tempers, aluminum alloys can be bent to sharp angles due to aluminum's excellent ductility. Common alloys like 6061 and 3003 can be bent to minimum inside angles as low as:
- 0.032" sheet: minimum 27 degree angle
- 0.050" sheet: minimum 30 degree angle
- 0.080" sheet: minimum 35 degree angle
- 0.125" sheet: minimum 45 degree angle
- 0.190" sheet: minimum 60 degree angle
Bendability decreases for thicker aluminum but remains better than steel. The minimum angle also depends on the work hardening and orientation of the grain structure. Annealing can restore ductility for sharper bends.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is challenging to bend with higher minimum bend angles than mild carbon steel. Austenitic stainless grades like 304 and 316 have a typical minimum inside bend angles around:
- 16 gauge (.060"): approximately 45 degrees
- 14 gauge (.075"): approximately 50 degrees
- 12 gauge (.105"): approximately 60 degrees
- 3/16" (0.1875"): approximately 75 degrees
Greater strength and poor flexibility limit the bending capability of stainless steel. Heat treating to anneal and re-soften the microstructure can allow tighter bending. Grain orientation also impacts the minimum bend angle.
Titanium
Strong and hard-to-deform titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-4V have some of the highest minimum bend angles, requiring specialized processes. Typical minimum angles for titanium are:
- 0.025" sheet: approximately 35 degrees
- 0.037" sheet: approximately 40 degrees
- 0.049" sheet: approximately 45 degrees
- 0.074" sheet: approximately 60 degrees
Most titanium bending requires hot working or specialized cold processes like high-pressure coin bending. Bend allowance rules must be carefully followed to avoid cracks.
Inconel/Nickel Alloys
Inconel and other nickel-chromium superalloys offer excellent heat and corrosion resistance but are incredibly challenging to deform without cracking. The minimum bend angles for these alloys are:
- 0.020" thickness: approximately 40 degrees
- 0.035" thickness: approximately 45 degrees
- 0.065" thickness: approximately 60 degrees
- 0.100" thickness: approximately 75 degrees
Various annealing heat treatments may allow sharper bending. Grain orientation significantly impacts the minimum bend angle with these materials.
Copper
Highly ductile copper and its alloys like brass can be bent to tight angles with minimums typically around:
- 0.015" sheet: approximately 22 degrees
- 0.031" sheet: approximately 27 degrees
- 0.062" sheet: approximately 35 degrees
- 0.125" sheet: approximately 45 degrees
Ductility decreases as copper work hardens. Intermediate annealing can restore sharp bending capability if needed. Grain structure has less influence than other metals.
Steel Plate and Structurals
For thick carbon steel plates, structural steel shapes, and tubing, minimum inside bend angles are:
- 1/2" plate: approximately 60 degrees
- 3/4" plate: approximately 70 degrees
- 1" plate: approximately 80 degrees
- 3x3" angle: approximately 70 degrees
- 4x4" angle: approximately 80 degrees
Dimensional change from deformation during bending increases stresses with plate thickness, necessitating larger minimum angles. External press braking is often used for structural steel versus conventional brake presses.
Refractory Metals
Columbium, molybdenum, tantalum, and tungsten refractory metals are extremely difficult to bend with minimum angles:
- 0.015" molybdenum: approximately 45 degrees
- 0.025" tungsten: approximately 40 degrees
- 0.015" tantalum: approximately 35 degrees
- 0.020" niobium: approximately 40 degrees
Their high strength and brittleness require hot working, specialized tooling, and well-controlled processes to avoid fracturing during bending.
More complex vital metals require larger minimum inside bend angles to avoid cracking and rupturing during fabrication. Ductile materials like aluminum and copper can be bent sharpest. Understanding these limitations enables proper process planning and tool selection.
评论
发表评论