Hardware Composition of Bluetooth Headset
Almost all the visible plastic and metal components, housings, buttons, fitting and decorative parts of a Bluetooth headset are manufactured using some form of injection molding for optimum aesthetics, ergonomics, quality, and cost. The internal electronics are then assembled and fit into these plastic molded structures.
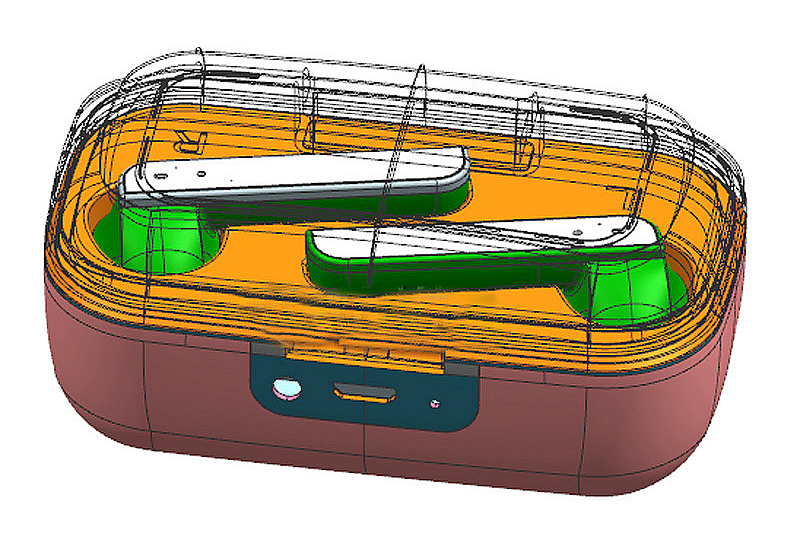
But it is mainly divided into three processes: plastic injection molding, zinc alloy die-casting, and metal injection molding.
Plastic Injection Molding Parts
The plastic injection molding accessories of the Bluetooth headset mainly include a thermoplastic injection molding body, such as a battery compartment, earplugs, sound insulation brackets, Etc. And thermoplastic injection molding accessories like Eartips, Protective Cases, Etc., details as follows:
Earbuds: The earbud housing that goes in/over the ear is injection molded to obtain the desired shape that fits comfortably in the ear. Various plastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and rubberized TPE can be used.
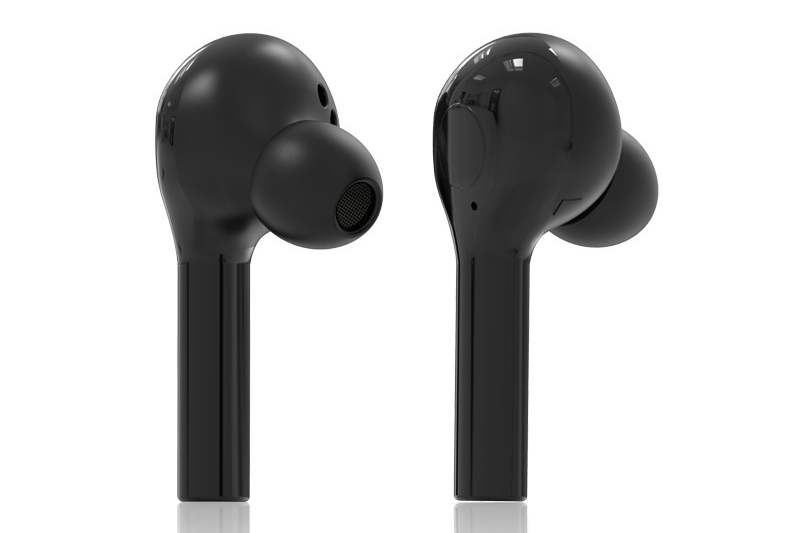

Eartips: The rubber/silicon ear tips that provide a snug seal inside the ear canal are molded from soft silicone or TPE material.
Housing/Shell: The main body/housing that contains the electronics is molded from sturdy plastic like ABS or polycarbonate. It requires molding of fine details for ports, buttons, etc.
Housing/Shell can also be made of zinc alloy shells with a certain weight and texture through the zinc alloy die-casting process.
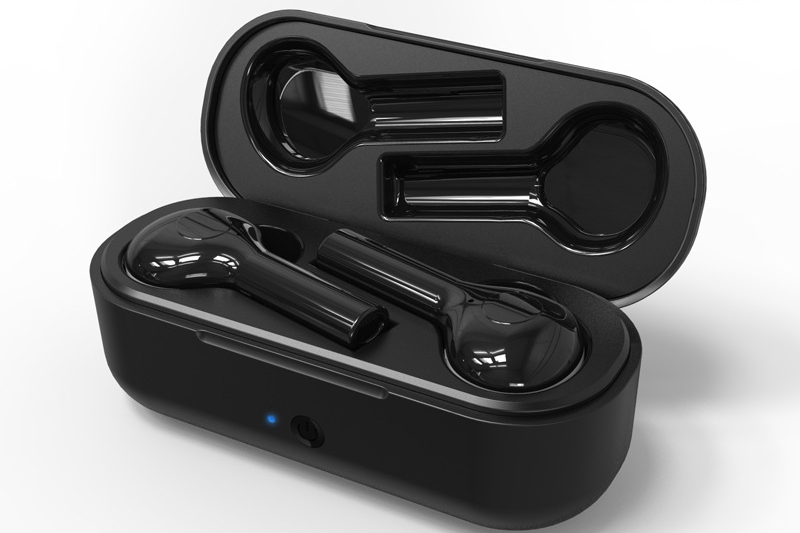

Stems: The stem/arm connecting the earbuds to the headband is often molded.
Control Buttons: The plastic buttons used for controlling audio, calls, etc, are molded from silicone or rubber for flexibility and tactile feel.
Battery Case - The plastic clamshell-style charging case is injection molded with details for properly housing and contacting the earbuds.
Decorative Covers - For a stylized look, decorative plastic covers can be molded and added to the headset.
Noise Isolation Mounts - Internal noise isolation mounts between components may be molded from rubber or silicone.
Plastic Injection Molding Introduction
Plastic injection molding is a standard manufacturing process used to efficiently produce high volumes of plastic parts. The process starts by melting down plastic pellets in the injection molding machine and injecting this molten plastic into a steel mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic solidifies, taking the shape of this mold cavity. The part is then ejected, and the mold closes for the next cycle. Various thermoplastic and thermoset plastics like ABS, nylon, and polyethylene are used. Injection molding allows complex 3D geometries with tight tolerances and minimum material waste. Parts have repeatable high quality. Automation makes injection molding cost-effective for the mass production of plastic components. It is famous for consumer goods, automotive parts, electronic enclosures, and other plastic items.
Zinc Die Casting Parts
Zinc die casting is commonly utilized where strength, intricate shapes, good surface finish, and RF properties are needed - like for structural frames, antenna covers, microphone arms, and decorative elements of a Bluetooth headset. It complements the plastic injection molded parts. Here are some of the critical components of Bluetooth headsets that are commonly manufactured using zinc die casting:
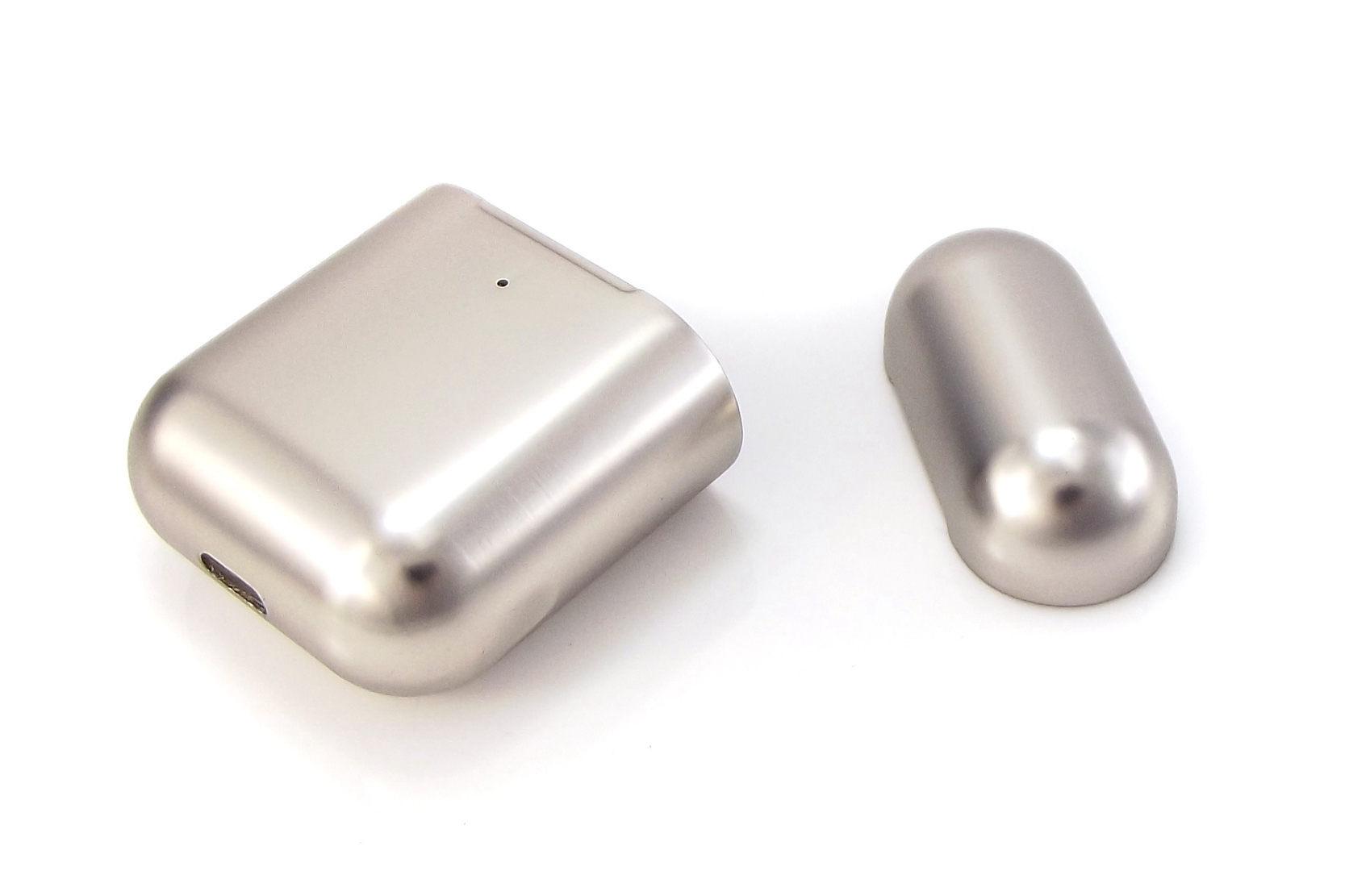

Frame/Housing: The main internal frame or housing that holds the circuit board and electronic components is often die-cast from zinc alloy. It gives sturdiness and rigidity. Frame/Housing can also be made of plastics.
Antenna Cover: The external cover for the Bluetooth antenna is usually a zinc die-casting part. This material allows sound RF signal transmission.
Microphone Arm: The microphone boom arm used to position the mic near the mouth can be a zinc die-cast part, providing the needed mechanical properties.
Structural Brackets: Internal structural brackets and supports connecting components are die-cast from zinc for strength while minimizing weight.
Charging Pins: The metal charging contact pins and ports in the headset and charging case may be zinc die-cast parts. Usually, the charging pin is manufactured by the insert molding process. Among them, the metal part is die-cast by zinc alloy, and the injection molding process completes the plastic part
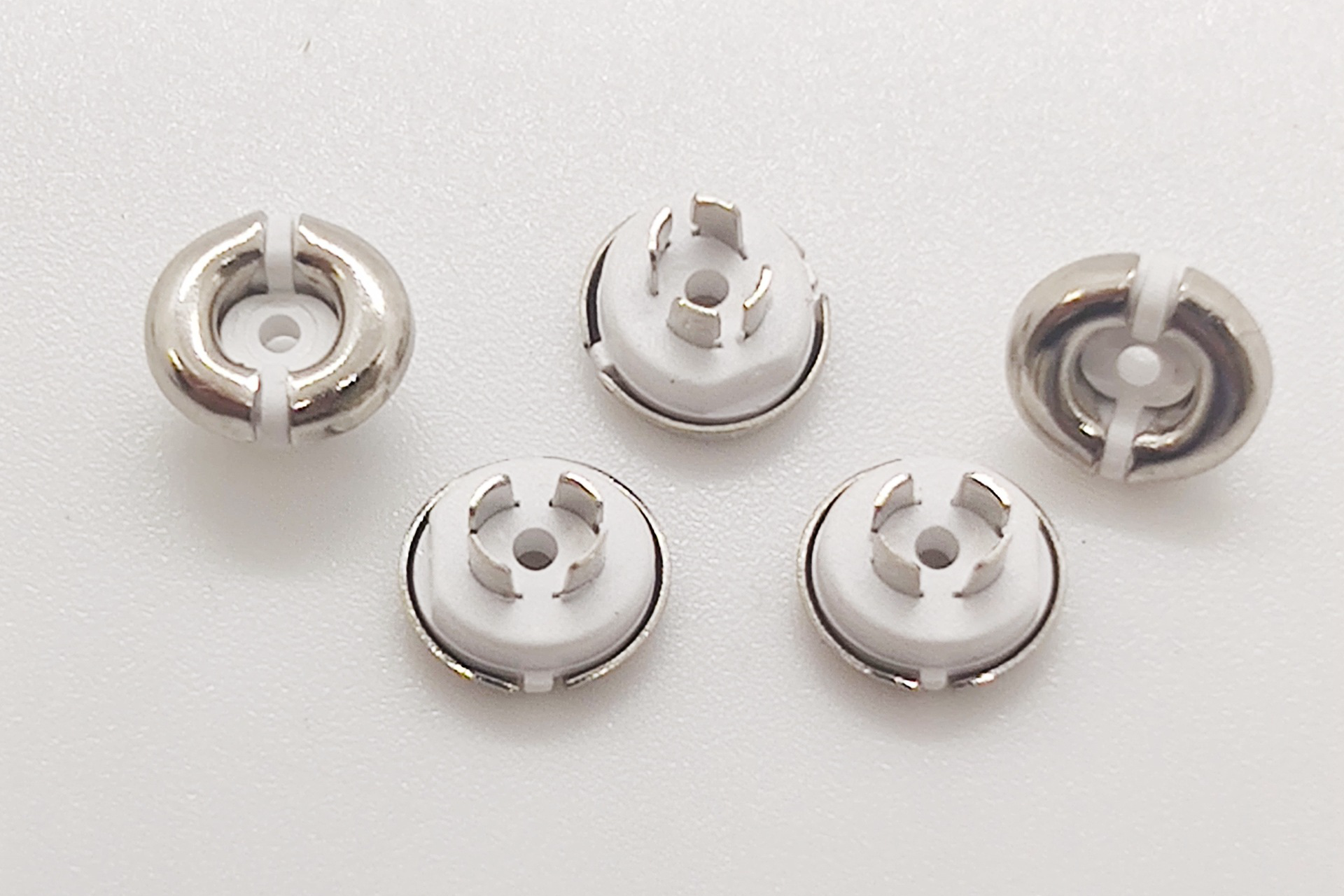

Screw Bosses: The threaded metal bosses molded into the plastic housing to accept fixing screws are often zinc die-cast inserts.
Shielding: Zinc die-cast parts are sometimes used as internal EMI shielding for the circuit boards and electronics.
Heat Sinks: Any small heatsinks required for dissipating heat from ICs or batteries may utilize zinc die casting.
Zinc Die Casting Introduction
Zinc die casting is suitable for high-volume precise, complex metal parts production. It involves forcing molten zinc alloy into reusable steel molds under high pressure and temperature. The zinc alloy solidifies, taking the shape of the die cavity. Zinc alloys provide good dimensional stability and shock and impact resistance. They also have excellent electromagnetic shielding properties. Parts can have thin walls and fine details. No further machining is required as die-cast parts can be produced with tight tolerances. Die casting offers faster production rates than sand casting or permanent mold casting. It is ideal for making metal components with accurate, smooth surfaces and thin sections across various industries, including automotive, electrical, and consumer products.
Metal Injection Molding Parts
While less common than plastic or zinc die casting, MIM does have some niche applications in Bluetooth headsets when small, complex metal components with good properties are required. The process allows intricate shapes and can consolidate assembly compared to machined metals. But the volumes must be high enough to justify the initial tooling costs.
Antenna: The Bluetooth antenna is sometimes metal injection molded from nickel-based alloys or other metal powders for good radio transmission properties.
Decorative Covers: Intricate and delicate metal logo inserts or covers can be MIM'ed from various alloys for aesthetics and branding.
Structural Components: Smaller internal structural brackets or supports may utilize MIM for added strength while minimizing size and weight.
Screws: Specialized small screws needed to assemble the headset components can be injection molded from metal powders.
Contacts: The charging or data transfer contact pins and terminals may be MIM parts to get the required mechanical and conductivity properties.
Shielding: In some cases, lightweight MIM shielding parts are used instead of zinc die casting for electromagnetic shielding of circuits.
Hinges: Small metal hinge components for folding/rotating headset parts can utilize MIM for high precision.
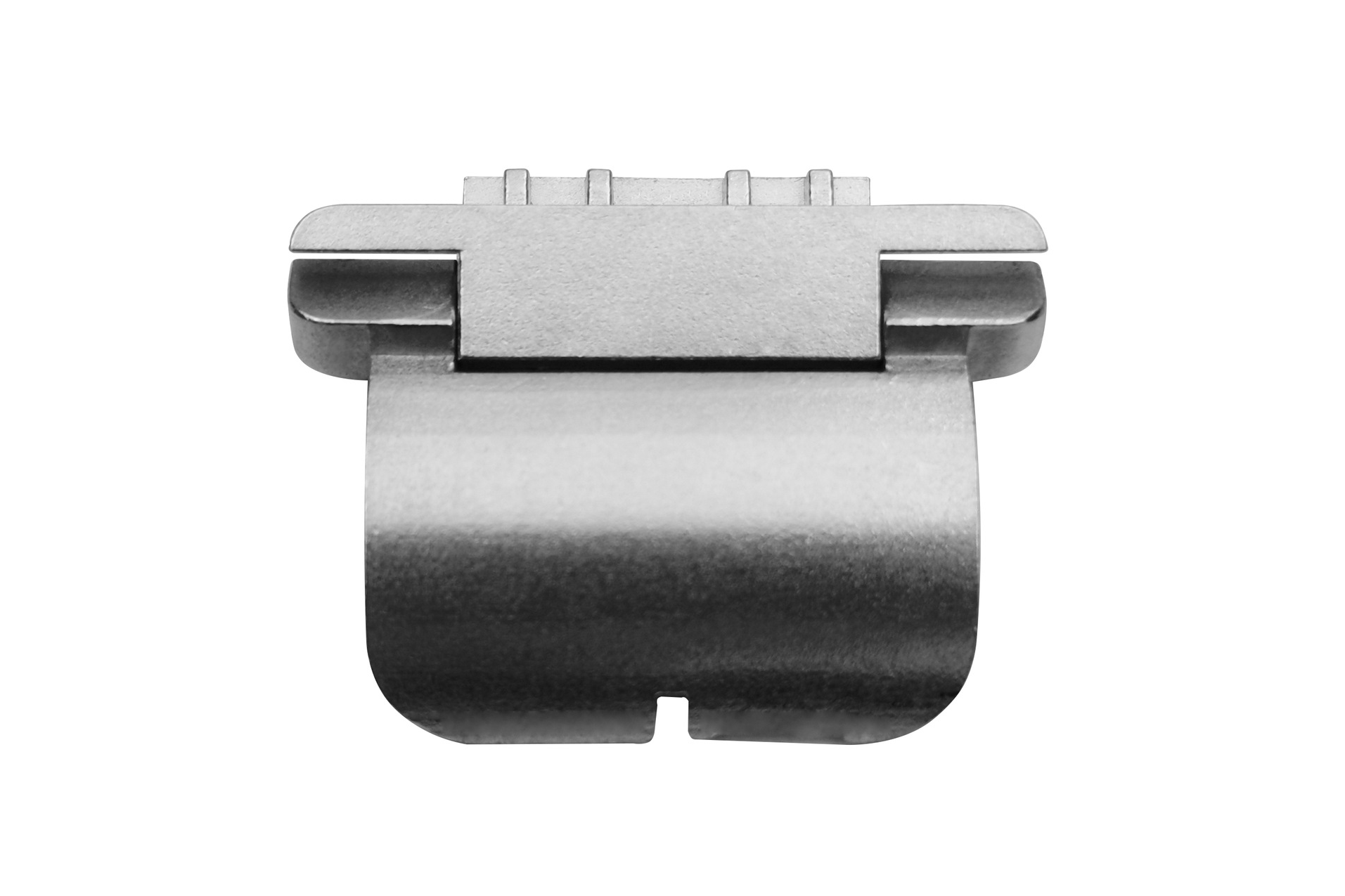

The hinge can also be produced by an injection molding process or a zinc alloy die-casting process, depending on the positioning of the product. High-end products generally use MIM technology, while low-end products can use injection molding technology. Of course, the cost is different.
What is Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Metal injection molding is a manufacturing process that allows complex, high-precision metal parts to be mass-produced at low cost. In MIM, a metallic powder is mixed with a thermoplastic binder to obtain a feedstock that can be injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The binder holds the shape. After molding, the green part is sintered to just below the melting point to burn off the binder and fuse the metal powder into a solid metal component. MIM combines the versatility of plastic injection molding with the superior material properties of metal alloys. It enables small, intricate metal components with good surface finishes to be molded to near-net shape. MIM is ideal for high volumes and is a cost-effective alternative to CNC machining metals.
Design Considerations of Bluetooth Headset Hardware
With these critical considerations during the design process, manufacturers can create comfortable, long-lasting headsets with the right style, functionality, and quality blend. Here are some key design considerations for the hardware components of Bluetooth headsets:
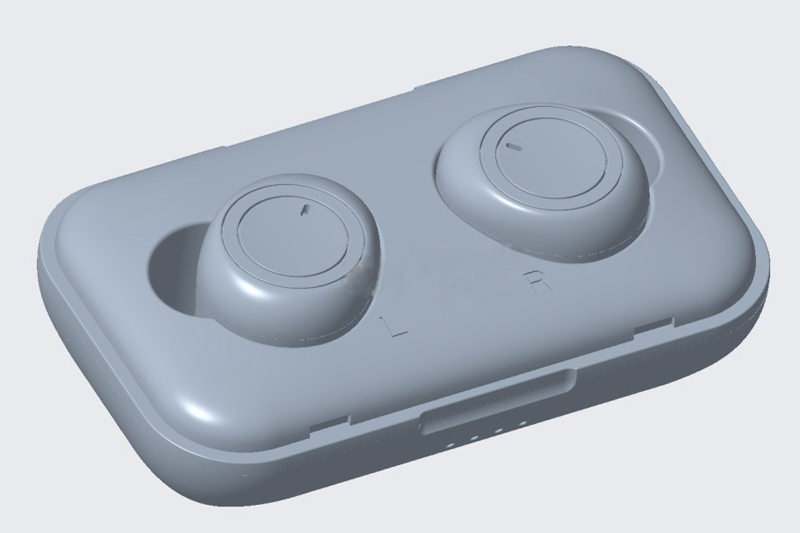

Ergonomics: The shape and size should allow for comfortable fit and wearability without causing pain or fatigue over extended use. Consider adjustable positioning, angled fittings, and lightweight materials.
Durability: Components like headbands, joints, and buttons should withstand drops, impacts, and other abuse from daily use. Use sturdy plastics, metal parts, and reinforcement joints.
Waterproofing: Exposure to sweat and the elements should be handled via waterproof coatings, sealed interfaces, and passive water drain holes.
Audio Quality: Speaker and acoustic components should be optimized for sound reproduction accuracy across different frequency ranges. Prioritize driver design.
Noise Isolation: Noise-isolating earbud shapes, passive dampening, and active noise cancellation help reduce ambient noise.
Battery Life: Balance battery capacity with weight; optimize power management features for standby and talk times. Allow for replaceable batteries.
Wireless Range: Antenna position, RF components selection, and Bluetooth protocol support determine the range from paired devices. Account for body shielding.
Ease of Controls: Buttons, touch controls, and mic need to be conveniently placed for easy access. Minimize accidental inputs.
Cost Optimization: Select inexpensive but proven components, reduce unnecessary features, and leverage common parts across models to minimize BOM cost.
Aesthetics: Styling, special coatings, and creative shapes can differentiate headsets and appeal to user preference.
Assembly: ensure the rationality of design and production precision and that the assembly gap between parts is within the control range.
Why Choose Neway for TWS Hardware
Finding the perfect accessories for your Bluetooth headsets can be tough. But Neway makes it easy. They've been crafting custom accessories for 30 years using the latest techniques: injection molding, precision casting, sheet metal work, 3D printing...you name it. Whatever unique accessory you dream up, Neway can make it happen. And the quality? Killer. Just check their reviews. Right now, they're offering 20% off your first order so you can try them out. There's never been a better time to ditch the boring old accessories and create something awesome for your brand. Let Neway bring your wildest ideas to life!

评论
发表评论